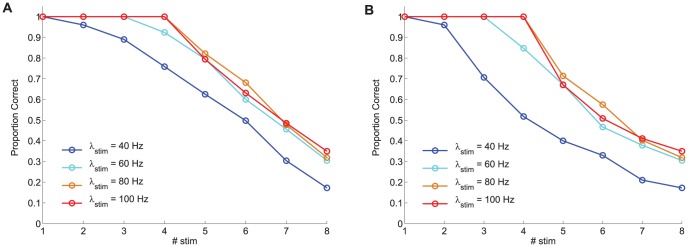
Figure 3. Model-based prediction of performance for different levels of external stimulation.
Model-based prediction of performance derived from computational simulations of a change detection task with  selective neural assemblies (
selective neural assemblies ( axis) simultaneously stimulated. Performance is calculated by assuming that an item is held in visual WM when its associated selective pool shows a mean persistent activity
axis) simultaneously stimulated. Performance is calculated by assuming that an item is held in visual WM when its associated selective pool shows a mean persistent activity 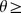 20 Hz during the last 300 ms of the delay period.
20 Hz during the last 300 ms of the delay period.  selective pools are stimulated at different amplitude levels
selective pools are stimulated at different amplitude levels 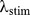 = 40 Hz, 60 Hz, 80 Hz, and 100 Hz. A Performance calculated as
= 40 Hz, 60 Hz, 80 Hz, and 100 Hz. A Performance calculated as 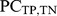 (Eq. 7), and B performance calculated as
(Eq. 7), and B performance calculated as 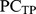 (Eq. 8). For both proposed performance estimates, performance decreases for larger set sizes but improves for larger stimulation amplitudes up to a value (
(Eq. 8). For both proposed performance estimates, performance decreases for larger set sizes but improves for larger stimulation amplitudes up to a value (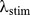 =
=  80 Hz) beyond which performance seems to converge.
80 Hz) beyond which performance seems to converge.