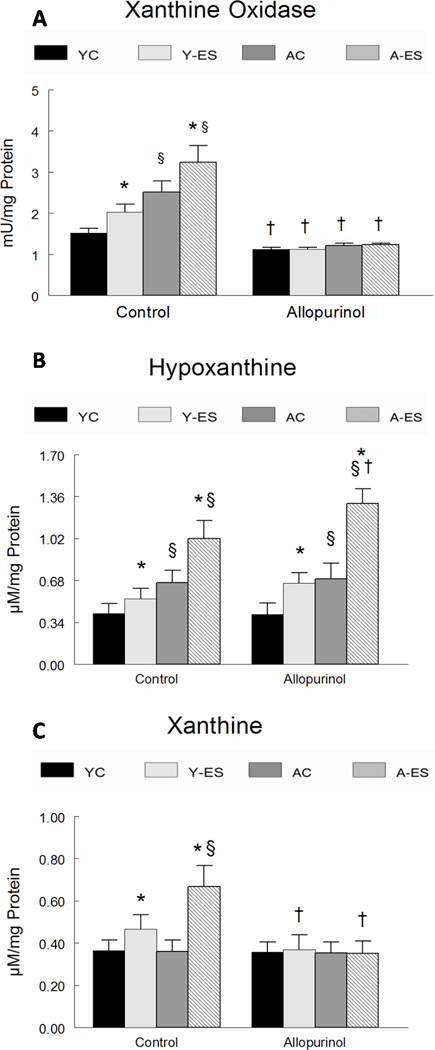
Figure 1. Allopurinol attenuated the increase in xanthine oxidase activity, hypoxanthine and xanthine associated with electrically evoked contractions.
(A) Xanthine oxidase activity was determined fluorometrically. Data are expressed as mU of activity per mg of total protein in gastrocnemius muscle homogenate. (B) Hypoxanthine and (C) xanthine levels were determined by a fluorometric assay. Data are expressed as µM concentration per mg of total protein in the gastrocnemius muscle homogenate. The normalized data for young control (YC), young electrically stimulated (Y-ES), aged control (AC) and aged electrically stimulated (A-ES) muscles are presented as mean ± SEM. * significant difference (P<0.05) between electrically stimulated muscles from contra-lateral control muscles; § significant effect of aging within the sham surgery or allopurinol treatment groups (P<0.05). † significant effect (P<0.05) of allopurinol treatment.