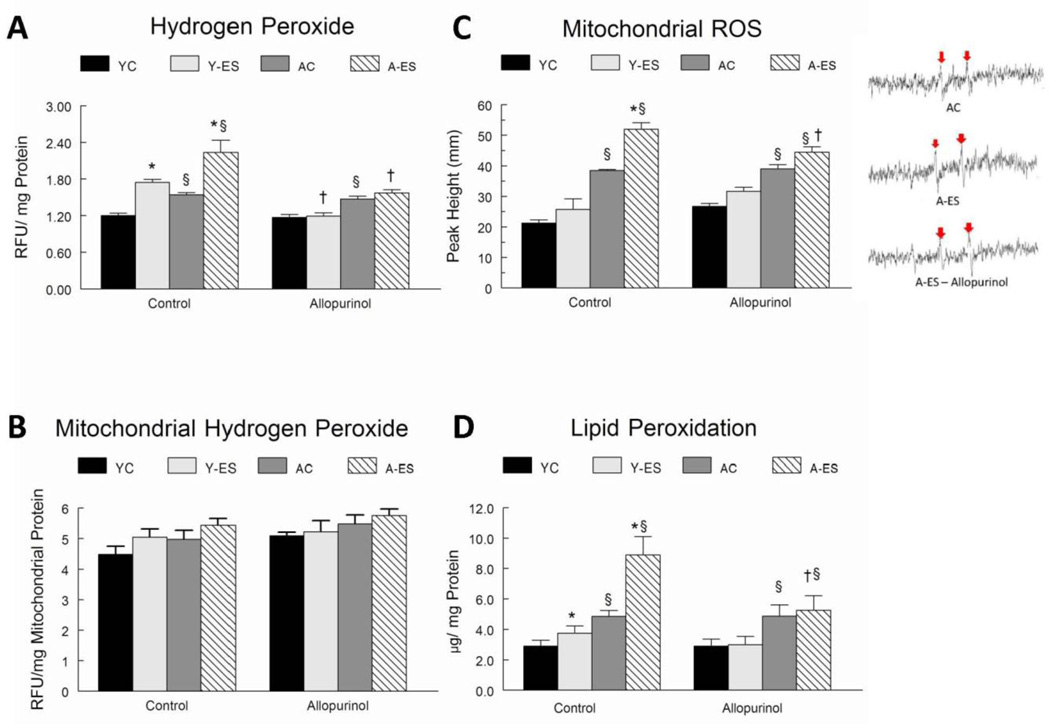
Figure 2. Inhibition of xanthine oxidase activity attenuated the increase in hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) concentration, lipid peroxidation and mitochondrial ROS radical production in response to in situ electrically stimulated contractions of aged mice.
(A) The H2O2 concentrations were determined a fluorometrically in total muscle homogenates. Data are expressed as Relative Fluorescent Units (RFU) per mg of total protein in gastrocnemius muscle homogenate. (B) The H2O2 concentrations were determined a fluorometrically in isolated mitochondrial homogenates. Data are expressed as Relative Fluorescent Units (RFU) per mg of total mitochondrial protein. (C) Mitochondria were isolated from control and electrically stimulated gastrocnemius muscles of young adult and old mice that received either placebo or allopurinol treatments. Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectroscopy was performed to index ROS radical generation. Isolated mitochondrial were incubated with 5,5-dimethyl-1-pyrroline-N-oxide in the presence or absence of excess complex I respiratory substrates glutamate and malate, incubated for 3 min at 37°C. Radical ROS levels were measured at room temperature with instrument settings of 1000 mW, modulation amplitude 1.0 G, receiver gain 1.00 × 104, conversion time 40.960 ms, time constant 40.960 ms and sweep time 41.943 ms, microwave frequency 9.752 GHz, Microwave power 126.90 mW. A representative spectra is shown and the red arrows indicate ROS radical spikes. (D) Data represent combined malondialdehyde (MDA) and 4-hydroxyalkenals (HAE) and are normalized to the total protein concentration in the gastrocnemius muscle homogenate. The normalized data for young control (YC), young electrically stimulated (Y-ES), aged control (AC) and aged electrically stimulated (A-ES) muscles are presented as mean ± SEM. * significant difference (P<0.05) of in situ electrically stimulated muscle from contra-lateral control muscle; § significant effect of aging within the sham surgery or allopurinol treatment groups (P<0.05). † significant difference (P<0.05) of the allopurinol treatment.