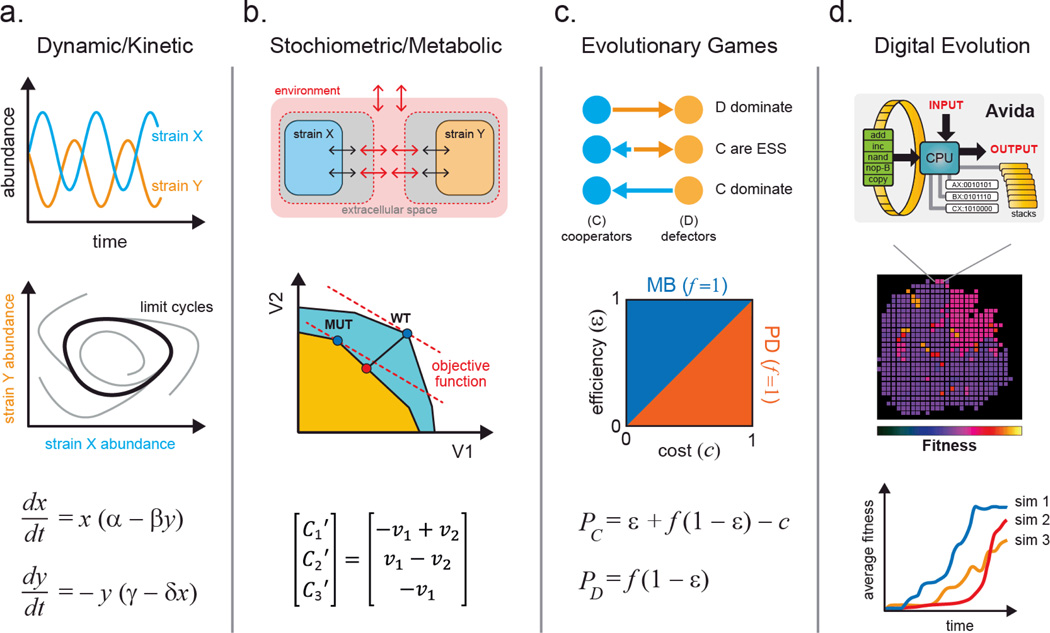
Figure 4.
The four main classes of quantitative models that are used to study microbial ecosystems. (a.) Kinetic models describe changes in system variables (e.g. abundance) with simple differential equations that can exhibit interesting dynamics such as oscillations and limit cycles. (b.) Stoichiometric models can be applied to study optimal metabolic flux using objective functions to guide the design of intercellular metabolite exchange. (c.) Evolutionary games can be used to analyze phenotypic strategies within a microbial community using payoff calculations. These models aid in elucidating key variables that influence the domination or coexistence of microbial strategies. (d.) Digital evolution systems help to simulate microbial evolution, traversal of fitness landscapes, development of complex traits, and contributions of epistatic and pleiotropic effects to fitness.