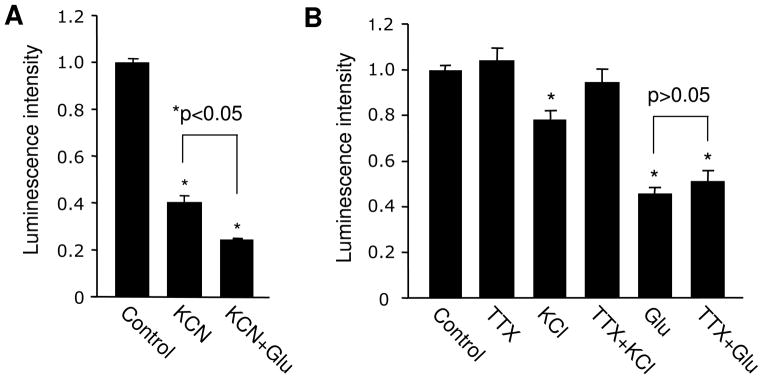
Figure 2.
Glutamate effect in ATP abundance is not caused by elevated neuronal firing. (A) Blockade of energy synthesis process by KCN lead to a dramatic reduction in ATP levels. In the presence of KCN, glutamate treatment remained to be able to cause ATP reduction. (B) Changes in ATP abundance following KCl-induced neuronal excitation were blocked by TTX; in contrast, blockade of neuronal firing had no effect on glutamate-dependent ATP regulation. *P<0.05, student’s t test.