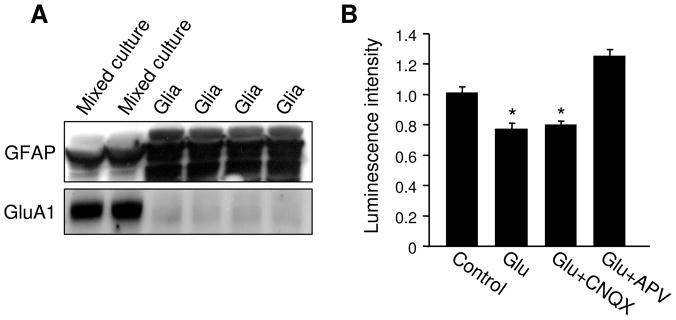
Figure 8.
Effect of glutamate on glial ATP. (A) Regular neuronal cultures (containing both neurons and glia) and glial cultures (neuron free) were lysed and analyzed by western blotting. Regular mixed neuronal cultures contained high levels of AMPAR subunit GluA1, but only a low level of the glial marker protein GFAP. In contrast, the glial cultures were enriched in GFAP, but only expressed minimal levels of glutamate receptors. (B) In glial cultures, glutamate induced a modest, but significant reduction in ATP amount. The change was blocked by NMDAR antagonist APV, but not AMPAR antagonist CNQX. *P<0.05, student’s t test.