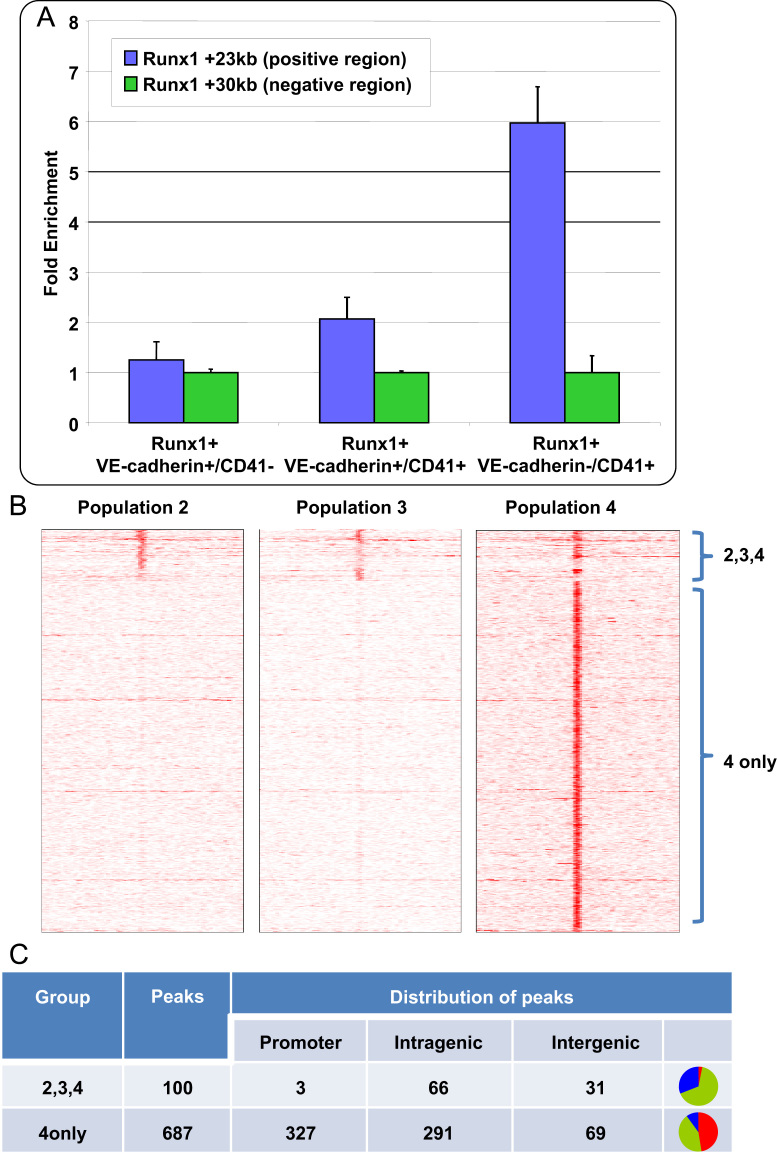
Fig. 3.
ChIP-Seq analysis of populations 2–4 permits genome-wide analysis of Runx1 recruitment to its target sites during early haematopoietic development. (A) Validation of Runx1 ChIP assays. Runx1 ChIP assays in populations 2–4 were validated using quantitative PCR with primer pairs for a region known to be bound by Runx1 (+23 kb, blue bars) and a negative control region (+30 kb, green bars) (Wilson et al., 2009). (B) Heatmaps displaying density profiles of Runx1 binding in populations 2–4 to all 787 peak regions, with the peak summit at the center shown with 5 kb flanking sequence either side. Few peaks occur in populations 2 and 3 with most peaks showing strong binding in population 4. (C) Analysis of peak locations with respect to genes. Peaks shared by all populations are rarely found in promoters whereas peaks found in population 4 are equally distributed between promoters and intragenic regions. The pie charts on the right show proportion of peaks in promoters (red), intragenic (green) and intergenic (blue).