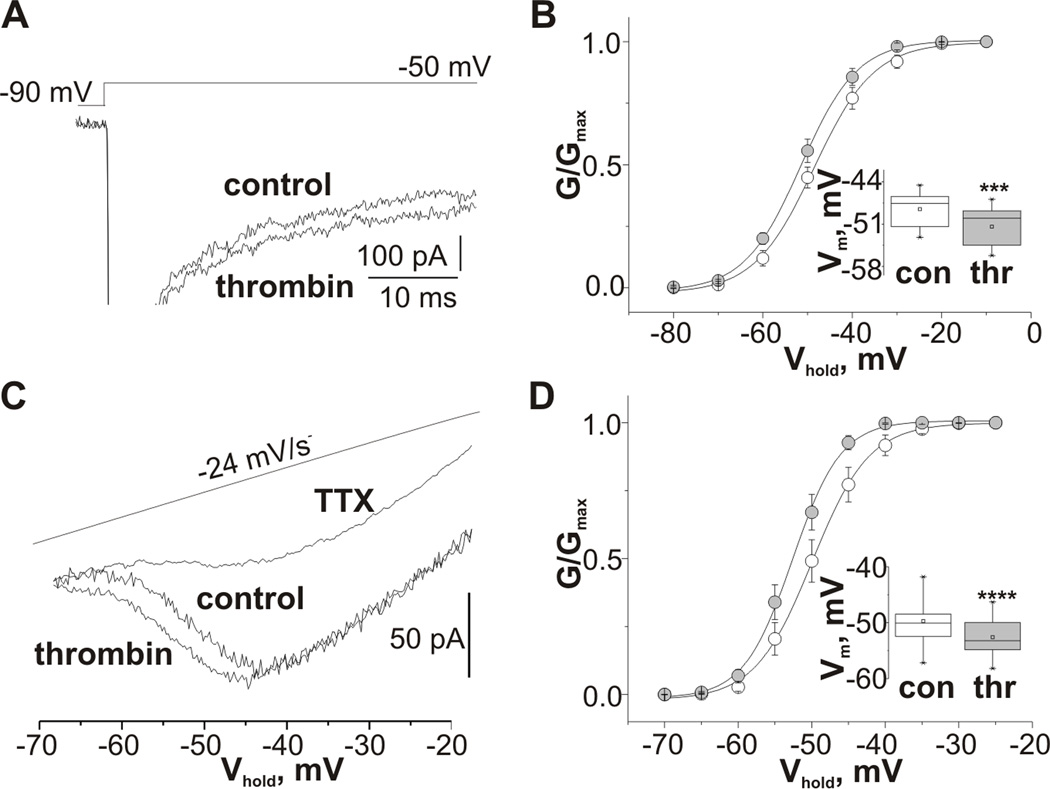
Figure 3.
Thrombin produces a hyperpolarizing shift of TTX-sensitive persistent sodium current activation. (A) Representative sodium current traces obtained under control conditions and in the presence of thrombin from CA3 pyramidal cell using the stimulus protocol shown in the upper panel. (B) Summarized voltage dependences of the normalized conductance of INap recorded using depolarizing step protocol from control cells (white) and in the presence of thrombin (grey) fitted by a Boltzmann function. (C) Representative sodium current traces obtained under control conditions, in the presence of thrombin or TTX from CA3 pyramidal cell using a slow ramp voltage protocol. (D) Summarized voltage dependences of the normalized conductance of INap recorded using a slow ramp voltage protocol from control cells (white) and in the presence of thrombin (grey) fitted by a Boltzmann function. Inserts represent summarized box plots of the mid-point potentials of the steady-state activation of INAp recorded using step (C) and ramp voltage protocols (D). Values are Mean ± SE.