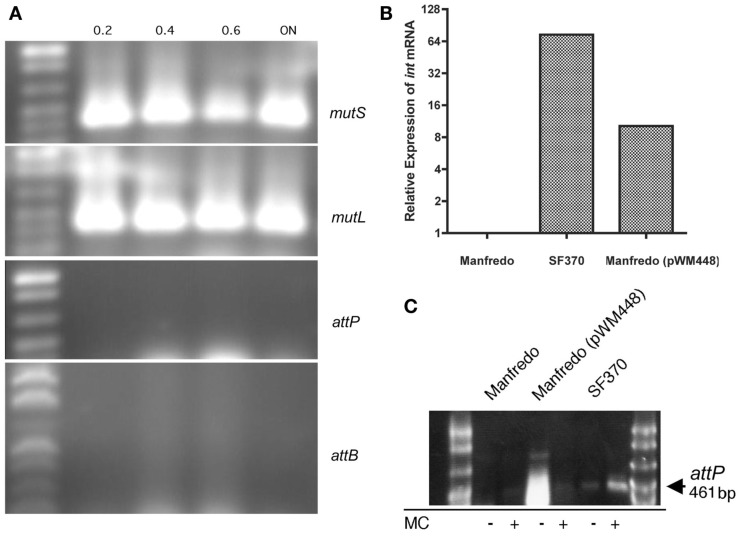
Figure 4.
Expression of mutL in Manfredo is independent of SpyCIM5 excision. (A) Expression of both mutS and mutL in strain Manfredo occurs without SpyCIM5 excision. PCR was used to amplify cDNA from strain Manfredo logarithmically growing cells or after overnight (ON) incubation (the absorbance at A600 when the cells were harvested is indicated above each sample). Both mutS and mutL were constitutively expressed while the SpyCIM5-associated sequences of attP and attB were never detected in Manfredo, indicating that SpyCIM5 excision does not normally occur in response to growth. (B) The SpyCIM1 integrase from SF370 was expressed in Manfredo by introduction of plasmid pWM448 containing the SpyCIM1 integrase ORF under control of the strong CAMP promoter. Gene int expression is absent from wild type Manfredo, and the target of the qRT-PCR amplification was the deleted region of the integrase ORF not present in Manfredo, confirming that expression was from the cloned SpyCIM1 gene. (C) The SpyCIM1 integrase mediates excision of SpyCIM5 in Manfredo. DNA was isolated from early logarithmic grown cells from Manfredo, SF370, or Manfredo (pWM448). PCR specific for attP, which is present only when the prophage-like element has excised from the mutS-mutL junction, produces no product in wild type Manfredo but appears after introduction of pWM448. Mitomycin C (MC), while stimulating the excision of the SpyCIM1 in strain SF370, inhibits the formation of attP in Manfredo (pWM448), suggesting inhibition of CAMP promoter activity.