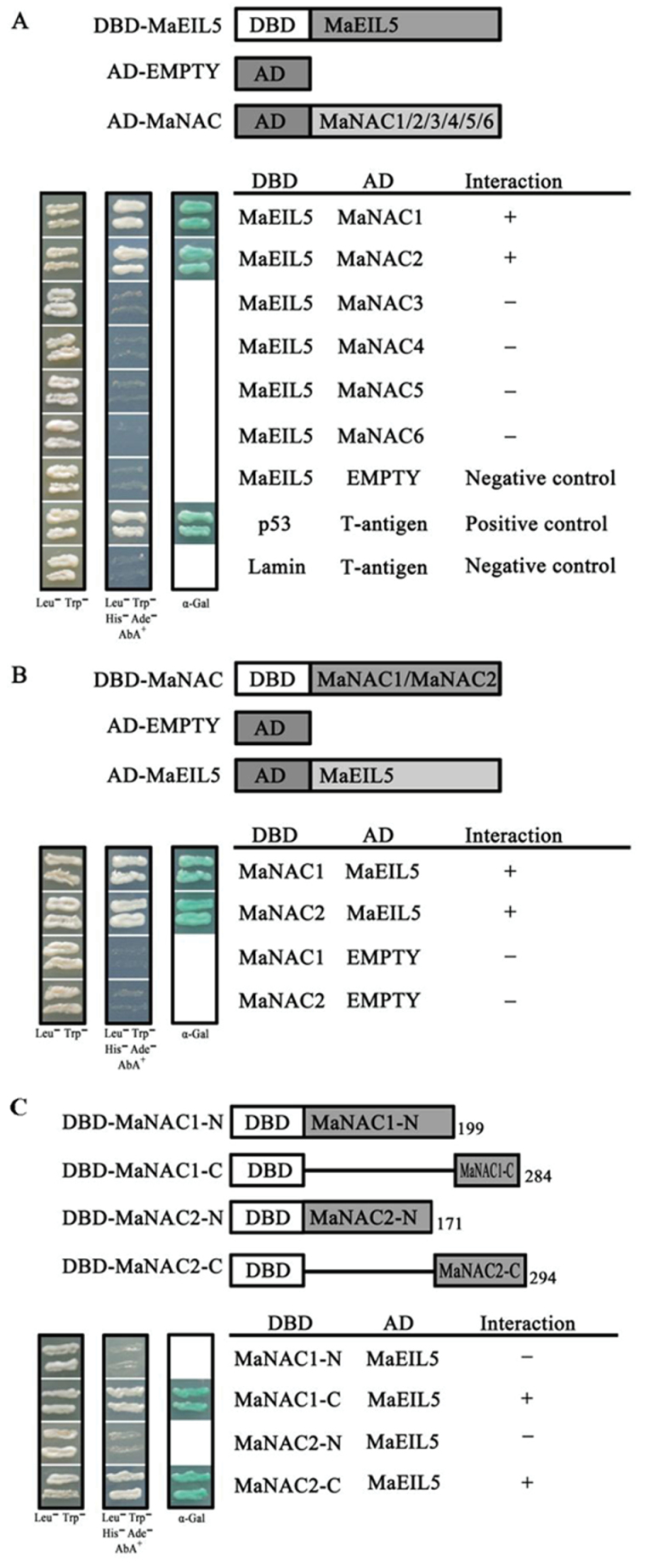
Fig. 9.
. Physical interactions between MaNAC proteins and MaEIL5 detected in Y2H assays. (A) The coding regions of MaNAC1–MaNAC6 were cloned into the pGADT7 vector to create the AD–MaNAC1 to -6 constructs, while the coding region of MaEIL5 was cloned into the pGBKT7 vector to create the DBD–MaEIL5 construct. Gold Y2H yeast strains were co-transformed with DBD–MaEIL5 and AD–MaNAC1 to -6, respectively. (B) The coding regions of MaNAC1/2 were cloned into the pGBKT7 vector to create the DBD–MaNAC1 and -2 constructs, while the coding region of MaEIL5 was cloned into the pGADT7 vector to create the AD–MaEIL5 construct. Gold Y2H yeast strains were co-transformed with DBD–MaNAC1 or -2 and AD–MaEIL5, respectively. (C) The N and C termini of MaNAC1 and MaNAC2 were tested for interaction with MaEIL5. Gold Y2H yeast strains were co-transformed with DBD–MaNAC1 or -2 derivatives and AD–MaEIL5, respectively. In (A), (B) and (C), the ability of yeast cells to grow on synthetic medium lacking tryptophan, leucine, histidine, and adenine but containing 125 µM Aureobasidin A, and to turn blue in the presence of the chromagenic substrate X-α-Gal, was scored as a positive interaction. Yeast cells transformed with pGBKT7-53+pGADT7-T, DBD–MaEIL5+pGADT7-T, or pGBKT7-Lam+pGADT7-T were included as positive or negative controls, respectively.