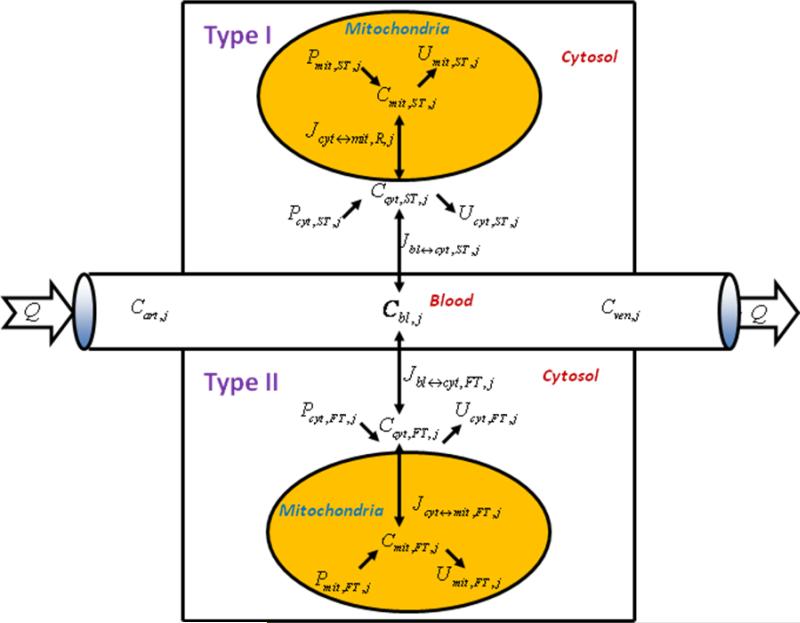
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of model structure. Whole skeletal muscle is composed of one blood domain and two tissue domains, corresponding to each muscle fiber, respectively. The fluid volume consists of capillary blood and interstitial fluid (ISF). Both muscle fiber types share a common blood supply. Each muscle fiber is compartmentalized as cytosol and mitochondria. Transport fluxes exist between blood and cytosol, and between cytosol and mitochondria. The species concentrations in tissue depend on reaction and transport fluxes.