Abstract
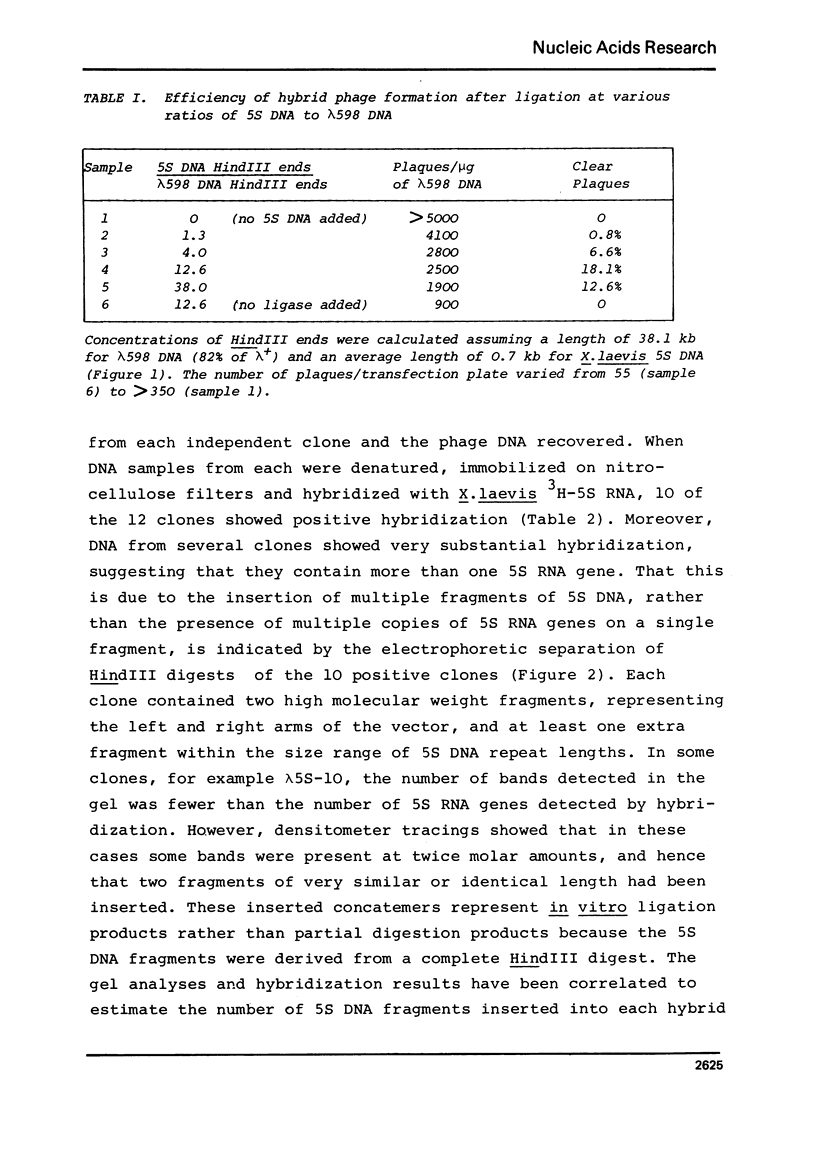
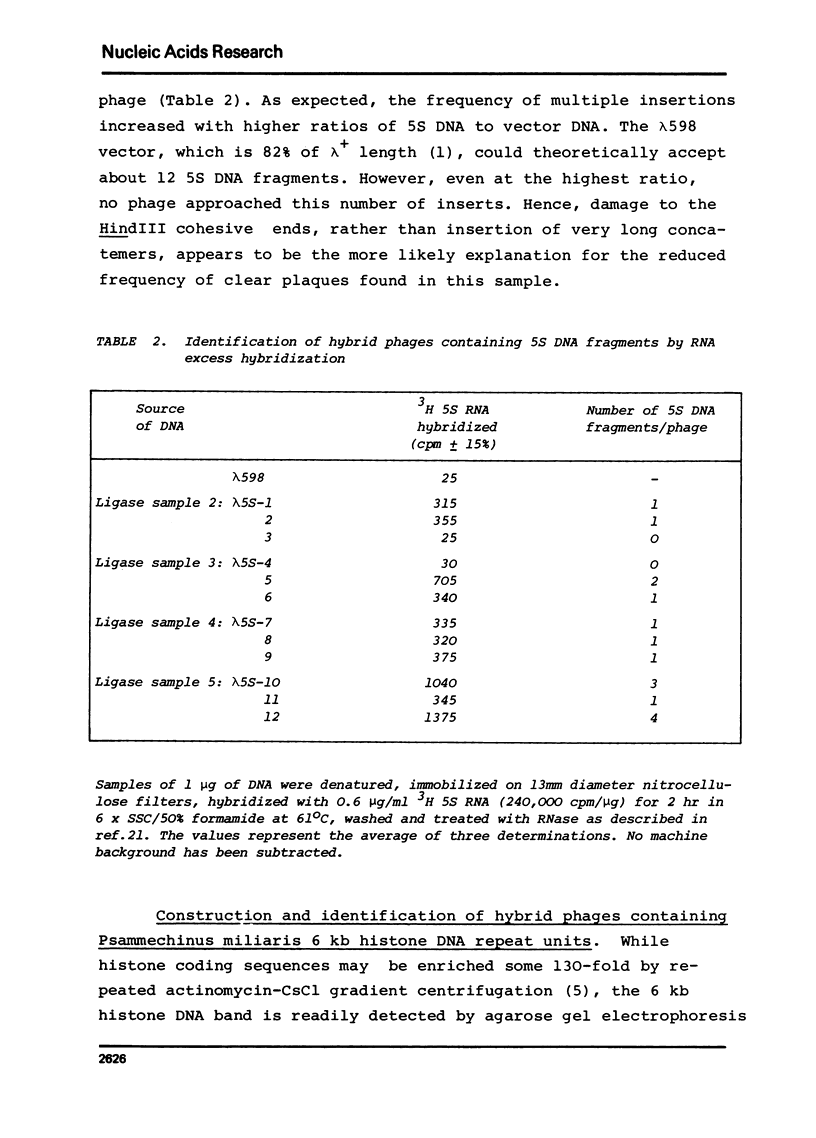
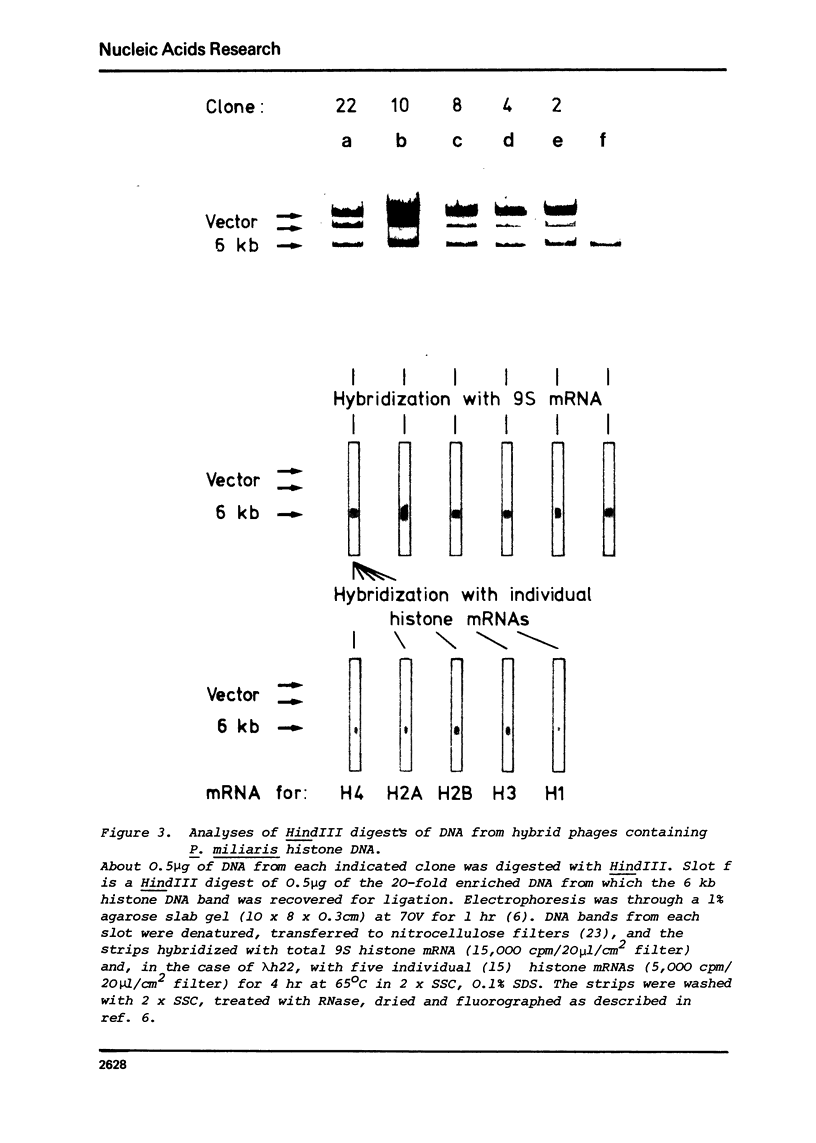
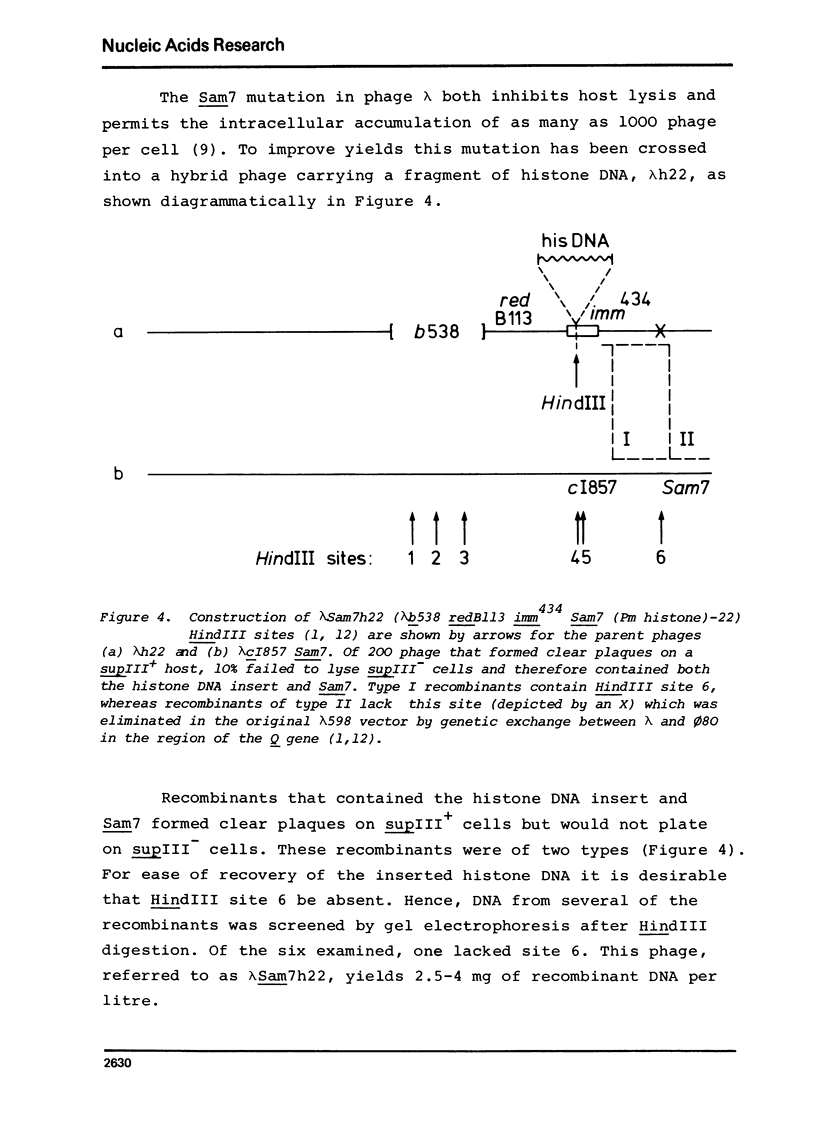
Highly purified HindIII restriction fragments of Xenopus laevis 5S DNA and of Psammechinus miliaris histone DNA have been covalently inserted into a derivative of phage lambda. This phage, genetically constructed by Murray et al. (1), contains only a single target for HindIII in the cI gene. Viable hybrid molecules were detected as clear plaque-forming phage after transfection of E. coli, the vast majority of which were shown by hybridization to be recombinants of the desired type. The lambdaSam7 mutation has been introduced into one hybrid phage containing histone DNA, thereby substantially increasing the yield of recombinant DNA.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg P., Baltimore D., Brenner S., Roblin R. O., Singer M. F. Summary statement of the Asilomar conference on recombinant DNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):1981–1984. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M. L., Sells B. H., Purdom I. F. Kinetic complexity of RNA molecules. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jan 14;63(1):21–39. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90519-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M. L., Wallace H., Sirlin J. L., Fischberg M. Localization of the ribosomal DNA complements in the nucleolar organizer region of Xenopus laevis. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1966 Dec;23:431–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M., Telford J., Weinberg E., Stafford D. Isolation and some properties of the genes coding for histone proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2900–2904. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brack C., Eberle H., Bickle T. A., Yuan R. A map of the sites on bacteriophage PM2 DNA for the restriction endonucleases HindIII and HpaII. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jun 14;104(1):305–309. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90016-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. D., Wensink P. C., Jordan E. Purification and some characteristics of 5S DNA from Xenopus laevis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3175–3179. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
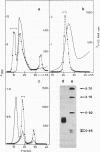
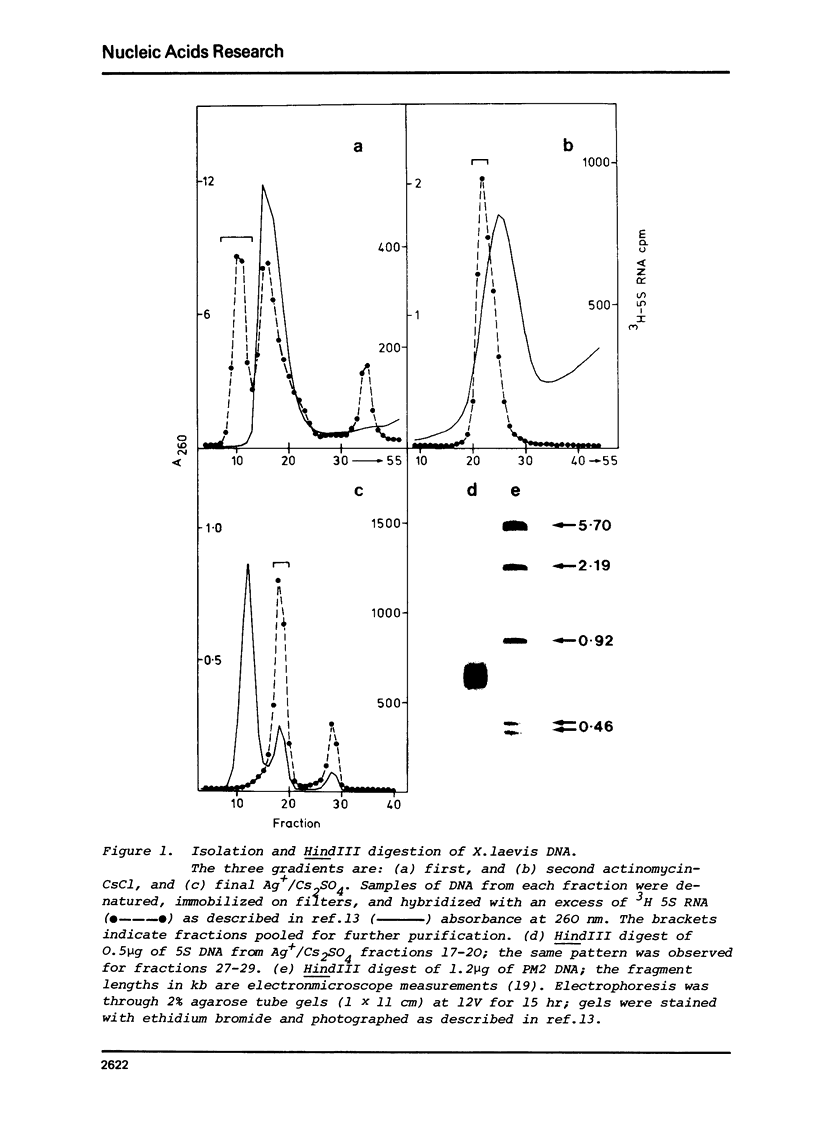
- Carroll D., Brown D. D. Repeating units of Xenopus laevis oocyte-type 5S DNA are heterogeneous in length. Cell. 1976 Apr;7(4):467–475. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90198-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarkson S. G., Birnstiel M. L., Serra V. Reiterated transfer RNA genes of Xenopus laevis. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):391–410. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarkson S. G., Kurer V. Isolation and some properties of DNA coding for tRNA1met from Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1976 Jun;8(2):183–195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N. The manipulation of genes. Sci Am. 1975 Jul;233(1):25–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFilippes F. M. A new method for isolation of a restriction enzyme from Hemophilus parainfluenzae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Jun 4;58(3):586–596. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80460-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dugaiczyk A., Boyer H. W., Goodman H. M. Ligation of EcoRI endonuclease-generated DNA fragments into linear and circular structures. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jul 25;96(1):171–184. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90189-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. R., Howe M. New mutations in the S cistron of bacteriophage lambda affecting host cell lysis. Virology. 1969 May;38(1):200–202. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90148-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross K., Probst E., Schaffner W., Birnstiel M. Molecular analysis of the histone gene cluster of Psammechinus miliaris: I. Fractionation and identification of five individual histone mRNAs. Cell. 1976 Aug;8(4):455–469. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90213-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray K., Murray N. E. Phage lambda receptor chromosomes for DNA fragments made with restriction endonuclease III of Haemophilus influenzae and restriction endonuclease I of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):551–564. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80086-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W., Gross K., Telford J., Birnstiel M. Molecular analysis of the histone gene cluster of psammechinus miliaris: II. The arrangement of the five histone-coding and spacer sequences. Cell. 1976 Aug;8(4):471–478. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90214-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streeck R. E., Philippsen P., Zachau H. G. Cleavage of small bacteriophage and plasmid DNAs by restriction endonucleases. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jun 15;45(2):489–499. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03574.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M., Davis R. W. Studies on the cleavage of bacteriophage lambda DNA with EcoRI Restriction endonuclease. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jan 25;91(3):315–328. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90383-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss B., Jacquemin-Sablon A., Live T. R., Fareed G. C., Richardson C. C. Enzymatic breakage and joining of deoxyribonucleic acid. VI. Further purification and properties of polynucleotide ligase from Escherichia coli infected with bacteriophage T4. J Biol Chem. 1968 Sep 10;243(17):4543–4555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]