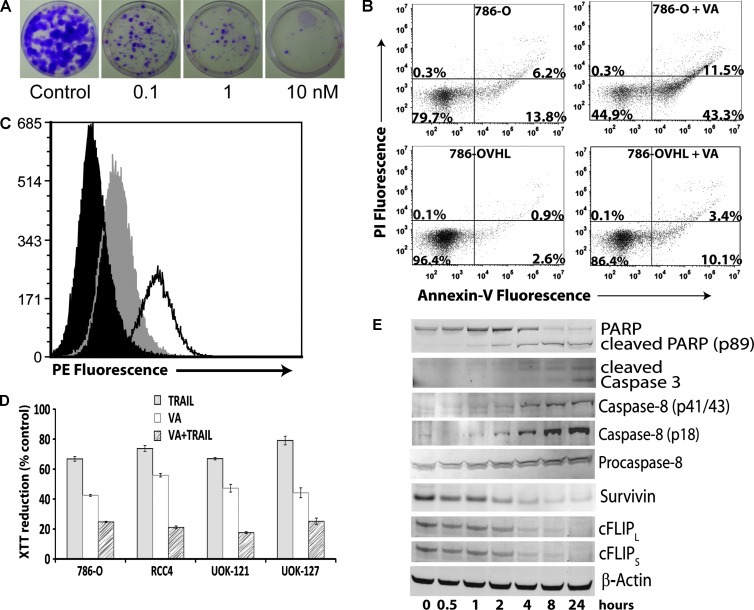
Figure 1.
Inhibition of proliferation of CCRCC cells by VA and induction of apoptosis. (A) Clonogenic survival assay of VA-treated 786-O cells. 786-O cells were treated with increasing concentrations of VA for 24 hours. After harvesting, cells were seeded at 100 cells/dish in 60-mm dishes in complete medium and allowed to grow for 14 days. Colonies were fixed and stained with crystal violet. (B) Flow cytometric analysis of PI and Annexin V double-stained 786-O and 786-OVHL cells. Cells were treated for 24 hours with 10 nM VA or DMSO. Percentages of cells in each quadrant shown are from one representative experiment. (C) 786-O cells were analyzed by flow cytometry for cell surface expression of DR5. Cells were stained with phycoerythrin (PE)-conjugated isotype control (black) or DR5-PE after control (gray) or VA (unshaded, 10 nM) treatment. (D) CCRCC cells were treated with control, VA (10 nM), TRAIL (20 ng/ml), or VA + TRAIL for 24 hours. Cell viability was assessed using 2,3-bis[2-methoxy-4-nitro-5-sulfophenyl]-2H-tetrazolium-5-carboxanilide reduction. (E) Time course of Western blot analysis of apoptosis signaling proteins in 786-O cells treated with 10 nM VA. A representative β-actin blot is shown as a loading control.