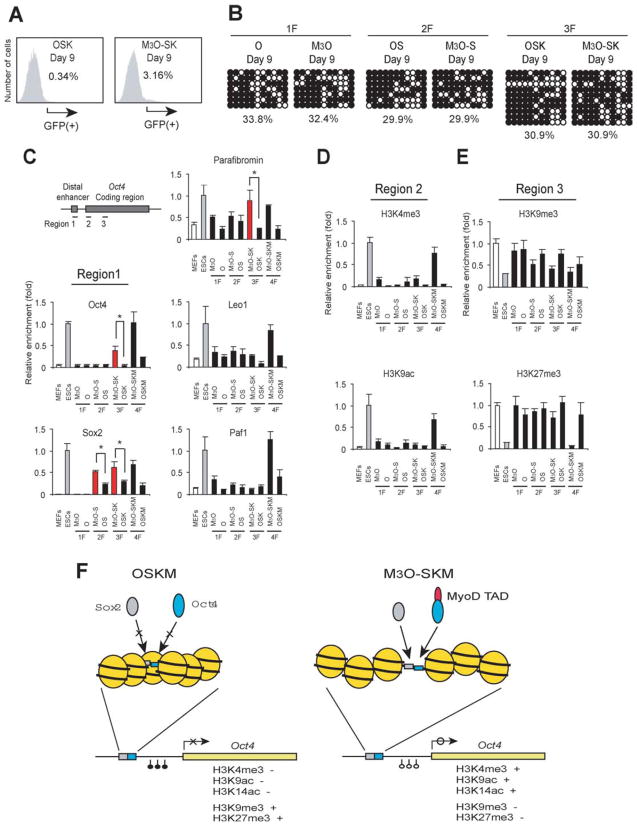
Figure 7.
Chromatin analyses of day 9 at the Oct4 gene comparing transduction of mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) with different gene combinations. (A): Flow cytometry of MEFs transduced with M3O-SK and OSK. (B): DNA methylation analysis by bisulfite sequencing. MEFs were transduced with one (1F), two (2F), or three (3F) transcription factor genes. (C): Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) studies on transcription factor binding at the distal enhancer. (D): ChIP analyses on histone modifications associated with active genes. (E): ChIP studies on histone modifications associated with suppressed genes. (F): Hypothetical summary of epigenetic remodeling induced by M3O-Sox2, Klf4, and c-Myc (right) in comparison to the lack of remodeling with Oct4, Sox2, Klf4, and c-Myc (left). Binding sites for Oct4 and Sox2 are located adjacent to each other at the distal enhancer of Oct4 [6]. Transduced Oct4 and Sox2 cannot bind to their respective binding sites (blue box and gray box, respectively) in the majority of MEFs with OSKM (O-MEFs) due to condensed chromatin. In contrast, M3O and Sox2 can effectively bind to each binding site in M3O-MEFs through the effects of the unidentified binding proteins to the MyoD transactivation domain. Recruitment of these proteins eventually contributes to DNA demethylation at the proximal promoter and a histone modification pattern typical of active genes at the coding region. Abbreviations: ESCs, embryonic stem cells; 1F, one transcription factor gene; 2F, two transcription factor gene; 3F, three transcription factor gene; GFP, green fluorescence protein; MEFs, mouse embryonic fibroblasts; O, Oct4; OS, Oct4 and Sox2; OSK, Oct4, Sox2, and Klf4; OSKM, Oct4, Sox2, Klf4, and c-Myc; S, Sox2; SK, Sox2 and Klf4; SKM, Sox2, Klf4, and c-Myc; TAD, transactivation domain.