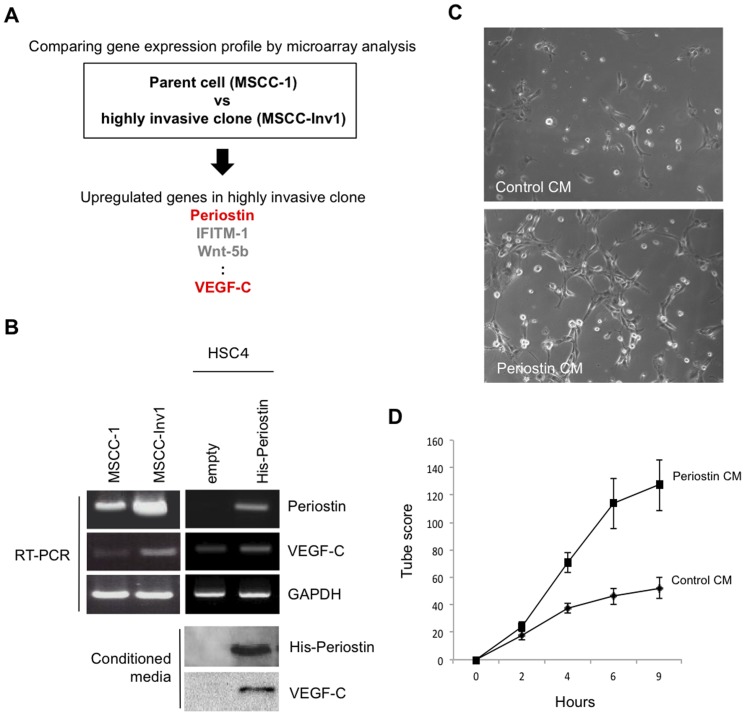
Figure 1. Involvement of VEGF-C promoted by Periostin overexpression on the tube formation of TR-LE cells.
(A) Schema shows the strategy to identify Periostin and VEGF-C by comparing the gene expression profile between the parent (MSCC-1 cells) and a highly invasive clone (MSCC-Inv1 cells). (B) Higher expression of VEGF-C mRNA in cells of the highly invasive clone MSCC-Inv1 and VEGF-C expression in periostin-overexpressing cells. HSC4 cells without periostin expression were transduced using a retroviral plasmid encoding hexa-histidine-tagged periostin. Periostin and VEGF-C mRNA expression levels in MSCC-1 cells, MSCC-Inv1 cells, empty vector-transfected HSC4 cells (empty), and periostin-overexpressing HSC4 cells (His-periostin) were examined by RT-PCR. GAPDH expression was used as a loading control. Conditioned media were collected from empty vector-transfected HSC4 cells (empty) and periostin-overexpressing HSC4 cells (His-periostin) after incubation for 4 days. Conditioned media were concentrated and analysed by western blotting for expression of His-periostin and VEGF-C in conditioned media. (C) Conditioned media from periostin-overexpressing cells promotes tube formation of lymphatic endothelial cells. Tube formation of TR-LE cells by adding conditioned media from periostin-overexpressing cells. TR-LE cells were seeded onto matrigel-coated wells in the presence of conditioned media from empty vector-transfected (control CM) or periostin-overexpressing (periostin CM) HSC4 cells. After incubation for 0–9 h, the lengths of the tube-like structures formed were evaluated. The figure shows the cells after incubation for 9 h. (D) The graph shows the tube scores after 0–9 h incubation of control CM or periostin CM. The bars show the average values and SDs from 3 independent experiments.