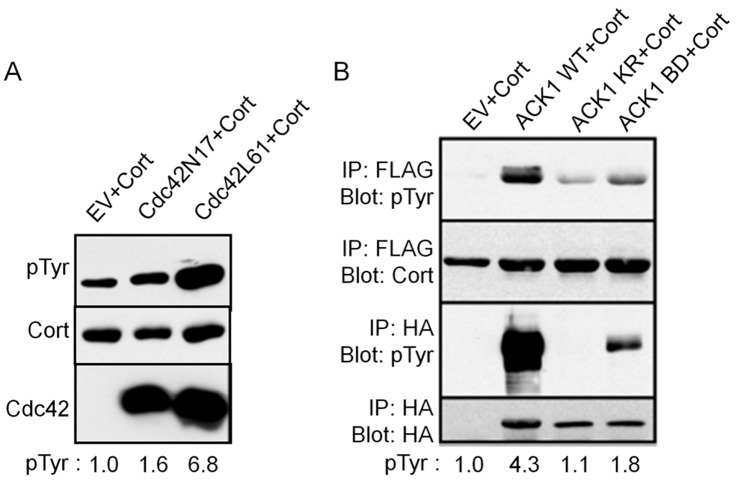
Figure 1. ACK1 mediates Cdc42-induced cortactin tyrosine phosphorylation.
(A) COS1 cells were cotransfected with FLAG-cortactin WT and Myc-tagged Cdc42 constructs as indicated. EV; empty vector. Cells were lysed 18 h after transfection, FLAG-cortactin immunoprecipitated and total cortactin tyrosine phosphorylation analyzed by Western blotting with a pan anti-phosphotyrosine antibody (pTyr). The blot was then stripped and reprobed for total cortactin levels (Cort). Equal amounts of total cell lysates were blotted in parallel with anti-Cdc42 antibodies to confirm GTPase expression. Ratios of tyrosine phosphorylated (pTyr) cortactin to total cortactin levels are indicated at the bottom. Blots are representative from ≥ three independent experiments. (B) ACK1 overexpression induces cortactin tyrosine phosphorylation. COS1 cells transfected with empty HA vector (EV), HA-ACK1 wild-type (WT), kinase dead (KR) (K-R mutation at amino acid 158 in the kinase domain) and a Cdc42 binding-null mutant (BD) (H-A mutation of codons 464 and 467 in the CRIB domain) were immunoprecipitated from lysates with anti-FLAG or anti-HA antibodies. FLAG-cortactin and HA-ACK1 proteins were evaluated for phosphotyrosine levels by Western blotting (pTyr). Expression levels for each protein were evaluated by stripping and reblotting with anti-cortactin and anti-HA antibodies as indicated. Ratios of tyrosine phosphorylated (pTyr) cortactin to total cortactin levels are indicated at the bottom. Blots are representative from three independent experiments.