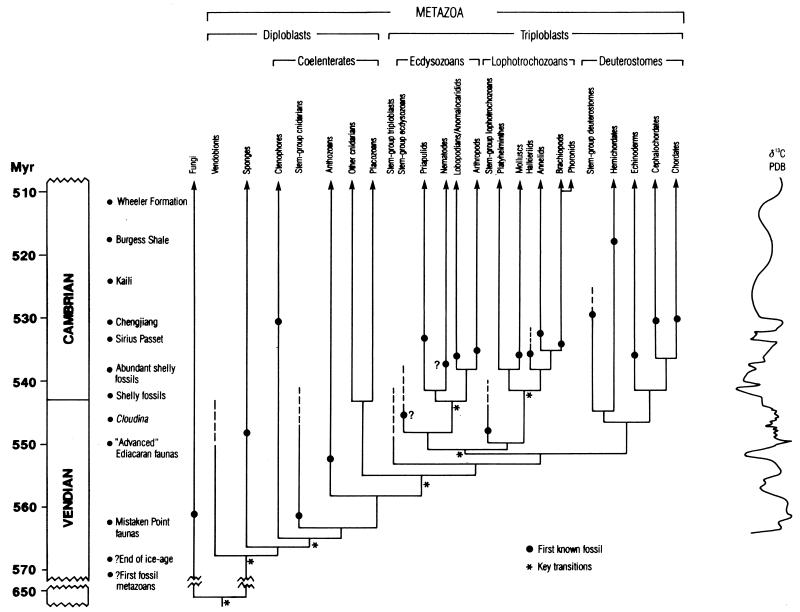
Figure 1.
Principal events across the Vendian-Cambrian boundary, spanning an interval of approximately 60 Myr (570–510 Myr), in the context of the early evolution of metazoans. On the left are denoted a series of important fossil assemblages, e.g., Burgess Shale, and various other significant events, e.g., cessation of ice age. To the right is the carbon isotope curve (redrawn from ref. 4), which provides an independent tool for correlation by chemostratigraphy and may also indicate substantial changes in ocean state with possible implications for evolutionary diversification. The evolutionary framework is largely based on molecular data (12, 19, 20), but the available fossil record not only gives a temporal perspective but also indicates major anatomical transitions that mark the emergence of distinct bodyplans. The sister-group of the Metazoa are the Fungi (35), and a possible time of divergence was ≈650 Myr ago. No fossil evidence for this event is yet available, and the early history of animals (≈650–570 Myr) is also cryptic. This is presumably because the earliest metazoans were microscopic and too fragile to fossilize readily. The most primitive animals in the fossil record may be represented by the vendobionts (36). Metazoans are otherwise divided into various major groupings, of which the most significant depends on the number of germ layers: respectively, two in the diploblasts and three in the triploblasts. The Ediacaran faunas postdate episodes of major glaciation and, with the exception of a few mineralized taxa (e.g., Cloudina), lack hard-parts. These Vendian-age assemblages comprise the problematic vendobionts, various coelenterates, and stem-group representatives of the three main groups of triploblast, referred to, respectively, as the ecdysozoans, lophotrochozoans, and deuterostomes. The process of exoskeleton molting, known as ecdysis, is a characteristic of the ecdysozoans. The most important group is the arthropods, and, possibly, they derive from a priapulid-like worm. Lophotrochozoans derive their name from a tentacular feeding organ (lophophore) found in some groups and the most widespread occurrence of a type of ciliated larva known as the trochophore. Lophotrochozoans are a diverse group encompassing the molluscs, annelids, and brachiopods. The ancestral form was probably rather slug-like. The deuterostomes are notably disparate and include the echinoderms and chordates.