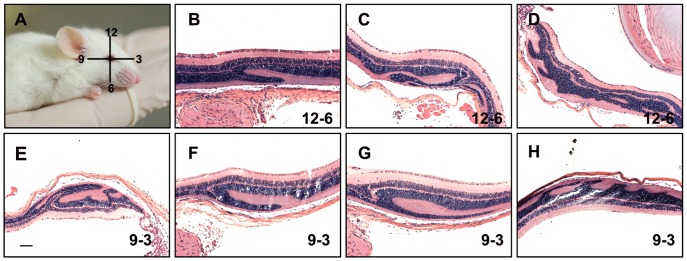
Figure 1. Retinal folding in two different orientations.
Retinas used in this experiment are from mice exposed for 24 hours to 1500 mg/kg of VGB and kept under constant light (A). Mouse illustration shows the orientation of the section planes with respect to the position of the eye globe relative to the body. A corneal scar was introduced with a cautery pen at the 12 o’clock position. This scar, visible under a magnifying lens, can used to orient the eye globe during embedding so that the plane of section is known. (B–D) Examples of retinal folds detected along the 12–6 o’clock plane. (E–H) Retinal folds along the 9–3 o’clock plane. Scale bar: 100 µm.