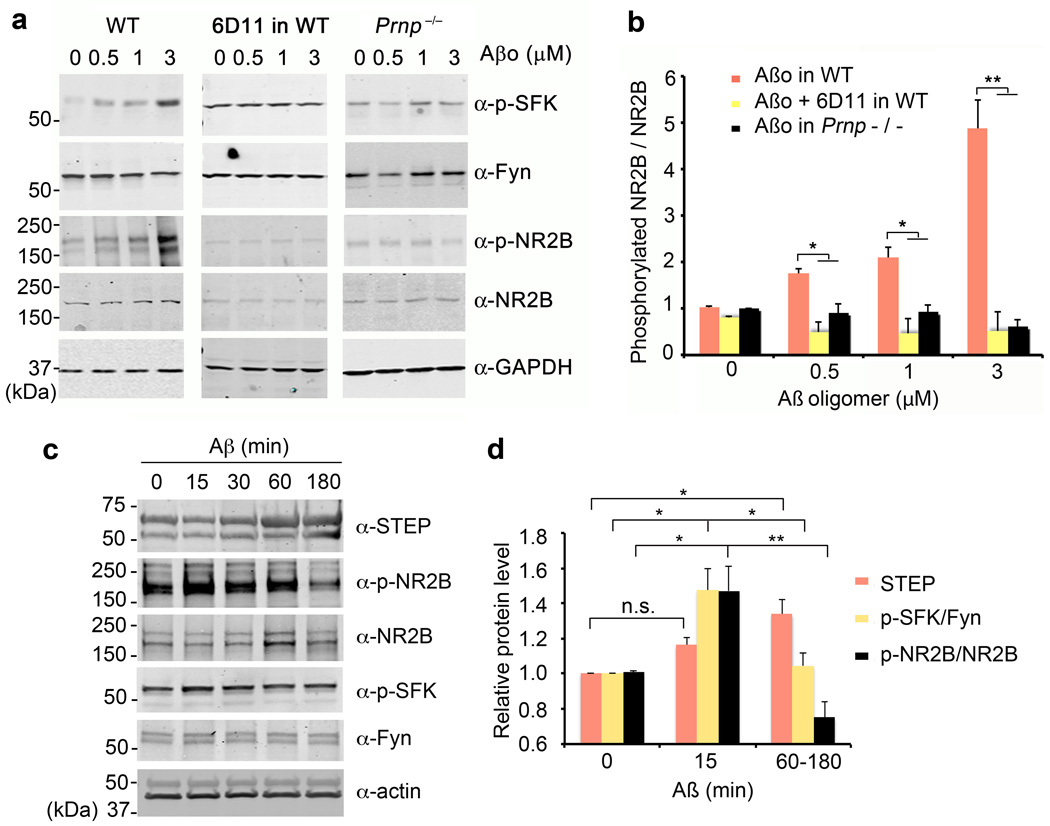
Figure 4. Aβo Increase NR2B Phosphorylation Transiently via PrPC and Fyn.
a Cortical neurons from E17 wild type or Prnp−/− mice after 21 DIV were treated with 0–3 µM Aβo for 20 min. Prior to Aβo exposure, the indicated cultures were pre-incubated with 10 µg/ml of 6D11 antibody for 1 h. Whole cell lysates were analyzed by anti-phospho-SFK (Tyr 416), anti-Fyn, anti-phospho-NR2B (Tyr 1472) or anti-NR2B immunoblot. GAPDH served as a loading control.
b Quantification of phospho-NR2B level in the lysate (from b) normalized to NR2B immunoreactivity. WT, n = 4; Prnp−/−, n = 4. Mean ± s.e.m. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; one-way ANOVA (F=36.98; df=11), with Tukey post-hoc comparisons.
c Cortical neurons from E17 wild type after 21 DIV were treated with 1 µM Aβo for 0–180 min. Whole cell lysates were analyzed by anti-STEP, anti-phospho-NR2B (Tyr 1472), anti-NR2B, anti-phospho-SFK (Tyr 416), or anti-Fyn immunoblot. Actin served as a loading control.
d Quantification of STEP level, phospho-SFK level normalized to Fyn immunoreactivity or phospho-NR2B level in the lysate (from c) normalized to NR2B immunoreactivity. Mean ± s.e.m. for 3 biologically independent replicates. n.s., not significant; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; one-way ANOVA (F=13.15; df=2), with Tukey post-hoc comparisons.