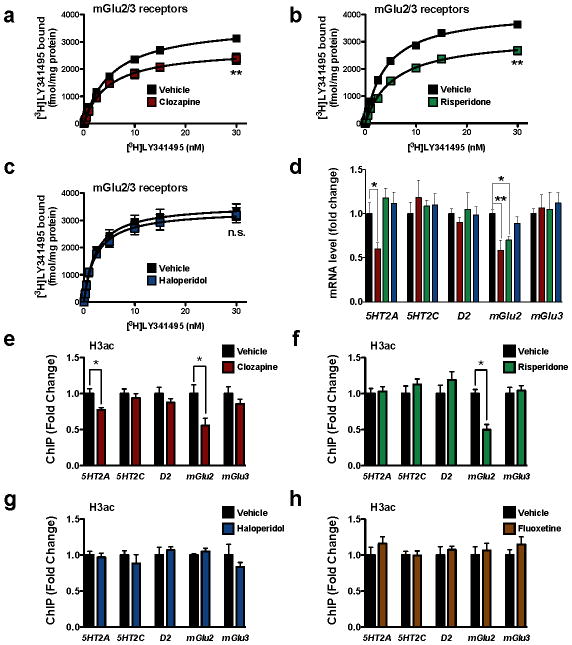
Figure 1. Decreased acetylation of histone H3 at the mGlu2 promoter by chronic treatment with atypical antipsychotic drugs in mouse frontal cortex.
(a–d) Chronic clozapine and risperidone, but not haloperidol, modulate the expression of mGlu2 in mouse frontal cortex. Mice were chronically (21 days) injected with vehicle (black), 10 mg/kg clozapine (red), 4 mg/kg risperidone (green), or 1 mg/kg haloperidol (blue), and sacrificed one day after the last injection. (a–c) [3H]LY341495 binding in mouse frontal cortex after vehicle or chronic clozapine (a), risperidone (b) or haloperidol (c). Effect of clozapine (n = 4 independent experiments performed in triplicate), F[2,95] = 65.34, P < 0.001; effect of risperidone (n = 6 independent experiments performed in triplicate), F[2,117] = 166.4, P < 0.001; effect of haloperidol (n = 6 independent experiments performed in triplicate), F[2,116] = 1.29, P > 0.05. Maximum number of binding sites (Bmax) for [3H]LY341495 obtained from individual saturation curves are decreased by chronic clozapine (t = 6.32; **P < 0.01), and risperidone (t = 6.53; **P < 0.01), but not haloperidol (t = 0.97; P > 0.05; n.s., not significant); two-tailed Student’s t-test. (d) Expression of 5HT2A, 5HT2C, dopamine D2, mGlu2, and mGlu3 mRNA in mouse frontal cortex assayed by qRT-PCR. Experiments were performed after vehicle or chronic clozapine, risperidone or haloperidol (n = 6 mice per group). Expression of 5HT2A, F[3,20] = 5.66, P < 0.01; Expression of 5HT2C, F[3,20] = 0.29, P > 0.05; Expression of D2, F[3,20] = 0.31, P > 0.05; Expression of mGlu2, F[3,20] = 6.62, P < 0.01; Expression of mGlu3, F[3,20] = 0.13, P > 0.05; one-way ANOVA. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; Bonferroni’s post hoc test of one-way ANOVA. (e–h) Decreased acetylation of histone H3 at the mGlu2 promoter by chronic clozapine (e) and risperidone (f), but not by haloperidol (g) or the antidepressant fluoxetine (h), in mouse frontal cortex. Mice were chronically (21 days) injected with clozapine (10 mg/kg), risperidone (4 mg/kg), haloperidol (1 mg/kg), fluoxetine (20 mg/kg), or vehicle, and sacrificed one day after the last injection. Fragmented chromatin was immunoprecipitated with antibody recognizing acetyl-histone H3 (H3ac), and the level of association of the 5HT2A, 5HT2C, dopamine D2, mGlu2, or mGlu3 promoters was measured by qPCR. Note also that acetylation of histone H3 at the 5HT2A promoter was decreased by chronic clozapine, but not by risperidone, haloperidol, or fluoxetine (n = 8 mice per group). H3ac at mGlu2 promoter: clozapine, t = 2.77; risperidone, t = 5.38; haloperidol t = 1.08. H3ac at 5HT2A promoter: clozapine, t = 2.96. The α value was corrected for multiple independent null hypotheses by using the Holm’s sequentially rejective Bonferroni method. *P < 0.011; two-tailed Student’s t-test. Error bars represent s.e.m.