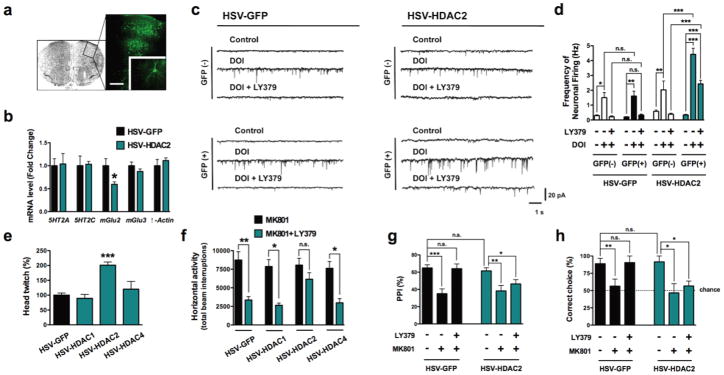
Figure 5. Viral over-expression of HDAC2 in frontal cortex decreases mGlu2-dependent behavioral function.
(a) Representative image of HSV-mediated transgene expression in frontal cortex. HSV-FLAG-HDAC2, which also expresses GFP, was injected into frontal cortex, and GFP expression was revealed by immunocytochemistry (Scale bar, 200 μm). Inset: GFP-expressing neuron.
(b) Viral-mediated over-expression of HDAC2 decreases expression of mGlu2 mRNA levels, and not 5HT2A, 5HT2C, mGlu3, or β-actin mRNA levels, in frontal cortex (n = 6 mice per group). Effect of HSV-HDAC2 on mGlu2 expression: t = 3.32. The α value was corrected for multiple independent null hypotheses by using the Holm’s sequentially rejective Bonferroni method. *P < 0.011; two-tailed Student’s t-test.
(c,d) Viral-mediated over-expression of HDAC2 attenuates the inhibition of 5HT2A receptor agonist DOI-induced sEPSC by LY379268. Sample traces (c). Whole-cell recordings from GFP-positive and GFP-negative neurons in acute cortical slices show that the increase in sEPSC frequency by the hallucinogenic 5HT2A agonist DOI (5 μM) is completely blocked by the mGlu2/3 agonist LY379268 (1 μM), while HSV-HDAC2 over-expression significantly decreases the effect of LY379268 on sEPSC frequency evoked by DOI in cortical pyramidal neurons (d). Effect of HSV-GFP (n = 2 mice per group, 10 neurons per mice) or HSV-HDAC2 (n = 3 mice per group, 10 neurons per mice), F[3,51] = 30.06, P < 0.001; effect of DOI and/or LY379, F[2,51] = 62.53, P < 0.001; two-way ANOVA. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; n.s., not significant; Bonferroni’s post hoc test of two-way ANOVA.
(e) Viral-mediated over-expression of HDAC2, but not HDAC1 or HDAC4, in frontal cortex significantly increases the head-twitch response induced by the hallucinogen DOI (0.5 mg/kg), (HSV-GFP, n = 10 mice; HSV-HDAC1, n = 5 mice; HSV-HDAC2, n = 5 mice; HSV-HDAC4, n = 5 mice). Effect of HSV-mediated over-expression, F[3,19] = 17.32, P < 0.001; one-way ANOVA. ***P < 0.001; Bonferroni’s post hoc test of one-way ANOVA.
(f) Viral-mediated over-expression of HDAC2, but not HDAC1 or HDAC4, in frontal cortex attenuates the inhibition of MK801-stimulated locomotor response by LY379268. Mice were administered LY379268 (8 mg/kg) or vehicle, followed by MK801 (0.5 mg/kg). The panel shows bar graph summary data of the total MK801-induced locomotor as a summation of horizontal activity from t = 15 to t = 120 min (n = 6-14 mice per group). Effect of HSV-mediated over-expression, F[3,61] = 2.76; P < 0.05; effect of MK801 and/or LY379, F[1,61] = 32.39, P < 0.001; two-way ANOVA. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; n.s., not significant; Bonferroni’s post hoc test of two-way ANOVA.
(g) Viral-mediated over-expression of HDAC2 attenuates the reversal of MK801-decreased prepulse inhibition (PPI) of startle by LY379268. Mice were administered LY379268 (5 mg/kg) or vehicle, followed by MK801 (0.1 mg/kg), (HSV-GFP, n = 25 mice per group; HSV-HDAC2, n = 35 mice per group). Effect of HSV-HDAC2, F[1,174] = 7.82, P < 0.01; Effect of LY379, F[2,174] = 35.26, P < 0.001; two-way ANOVA. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; n.s., not significant; Bonferroni’s post hoc test of two-way ANOVA.
(h) Viral-mediated over-expression of HDAC2 attenuates the reversal of MK801-impaired delayed alternation memory performance (percentage of correct trials at 10 s delay) by LY379268. Mice (HSV-GFP and HSV-HDAC2) made significantly fewer correct choices after the 40 s delay relative to the 10 s delay (see Supplementary Fig. 5h). Mice were administered LY379268 (5 mg/kg) or vehicle, followed by MK801 (0.5 mg/kg), (HSV-GFP, n = 10 mice per group; HSV-HDAC2, n = 16 mice per group). The dashed line indicates chance performance. Effect of HSV-HDAC2, F[1,67] = 5.28, P < 0.05; Effect of LY379, F[2,67] = 14.02, P < 0.001; two-way ANOVA. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; n.s., not significant; Bonferroni’s post hoc test of two-way ANOVA. Error bars represent s.e.m.