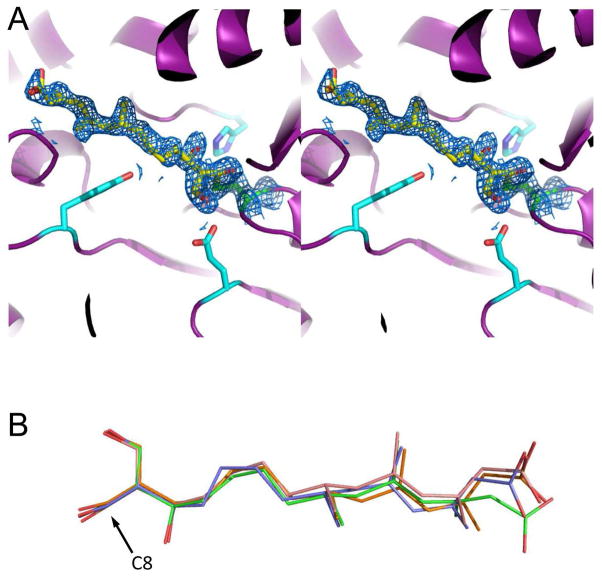
Figure 3.
1.95 Å structure of E. faecalis mvaS covalently modified by hymeglusin. Crystals of E. faecalis mvaS that had been briefly incubated with hymeglusin were produced as described in methods and used to collect monochromatic diffraction data. Following structure solution by molecular replacement, electron density maps were calculated that allowed modeling of bound ligand in each of the four crystallographically independent active sites. (A) Stereogram of the mvaS active site for chain A. Protein backbone is depicted in cartoon format (purple), while the sidechains of Glu79, Tyr143, and His233 are shown as cyan sticks. The catalytic Cys111 is colored green, and carbon atoms of covalently-bound hymeglusin are colored yellow. 2Fo-Fc map (blue mesh at 1.1σ contour) of the refined structure corresponding to the Cys111 thiolate-hymeglusin adduct is also shown. (B) Overlay of hymeglusin molecules as modeled in chains A-D, colored blue, green, orange, and red, respectively. The position of C8, which forms a covalent bond with the thiolate sulfur derived from Cys111, is indicated with an arrow. Additional information for all four active sites can be found in Supplemental Figures 2–4.