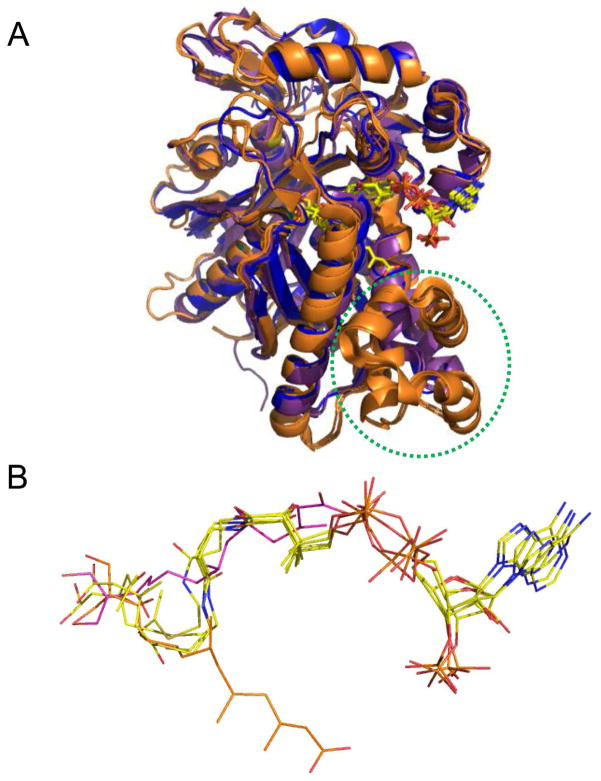
Figure 6.
Comparison of available ligand-bound structures for E. faecalis and S. aureus mvaS and B. juncea HMG-CoA synthases. (A) Superposition of enzyme monomers from E. faecalis mvaS bound to hymeglusin (PDB code 2V4X) and acetyl-CoA (PDB code 1YSL, chain B), S. aureus mvaS bound to acetoacetyl-CoA (PDB code 1TXT, chain A), and B. juncea HMG-CoA synthase bound to hymeglusin (PDB code 2F9A), acetyl-CoA (PDB code 2FA3), and HMG-CoA (PDB code 2FA0). The E. faecalis and S. aureus structures are shown in purple and blue, respectively, while the B. juncea structures are drawn in orange. The location of the helical insertion domain that is only found in the eukaryotic enzyme is highlighted with a dashed green circle. The positions of the bound ligands/inhibitors are shown in ball and stick format. Note that each of these ligands/inhibitors adopts the same positional conformation, except for hymeglusin when bound to B. juncea HMG-CoA synthase. Instead, this inhibitor binds to an opposing face of the active site funnel when compared to the CoA derivatives. (B) Magnified views of the positions of each of the ligands/inhibitors from panel B as they lie within the superimposed enzyme active sites. All CoA-derived ligands are colored with their carbon atoms in yellow, while hymeglusin as found in the E. faecalis and B. juncea enzymes is colored with purple and orange carbon atoms, respectively.