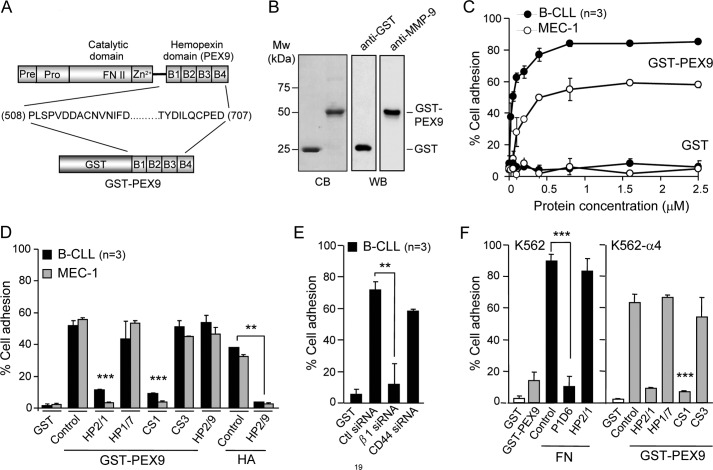
FIGURE 1.
B-CLL cells bind to immobilized GST-PEX9 via α4β1 integrin. A, a schematic drawing shows the various domains of proMMP-9 and the four structural blades (B1-B4) of the hemopexin domain (PEX9). The GST fusion protein prepared in this study (GST-PEX9) contained amino acid residues 508–707 of proMMP-9. B, shown is analysis of GST-PEX9 by 10% SDS-PAGE followed by Coomassie Blue staining (CB) or Western blotting (WB) with anti-GST or anti-MMP-9 polyclonal antibodies. C, BCECF-AM-labeled primary B-CLL cells (patients 5, 7, 10) or MEC-1 cells (3 different experiments) were added to wells coated with the indicated concentrations of GST or GST-PEX9. After 60 min at 37 °C, attached cells were quantitated using a fluorescence analyzer. D, BCECF-AM-labeled cells with or without previous incubation with the indicated Abs or peptides were added to wells coated with 0.2 μm (B-CLL, patients 3, 10, 15) or 0.4 μm (MEC-1, 3 different experiments) GST-PEX9 or 4 μm hyaluronic acid (HA), and adhesion was quantitated as explained. E, B-CLL cells (patients 11, 17, 18) were transfected with control siRNA or siRNA for the β1 integrin subunit or for CD44, labeled with BCECF-AM, and tested for adhesion to 0.2 μm GST-PEX9 as explained. F, 1 × 105 BCECF-AM-labeled K562 cells, transfected or not with α4 integrin subunit and preincubated or not with the indicated Abs or peptides, were added to wells coated with either 0.2 μm GST, 0.036 μm fibronectin (FN), or 0.4 μm GST-PEX9. After 60 min, adhesion was quantitated as explained. All values represent the percentage of the total number of cells added. **, p ≤ 0.01; ***, p ≤ 0.001.