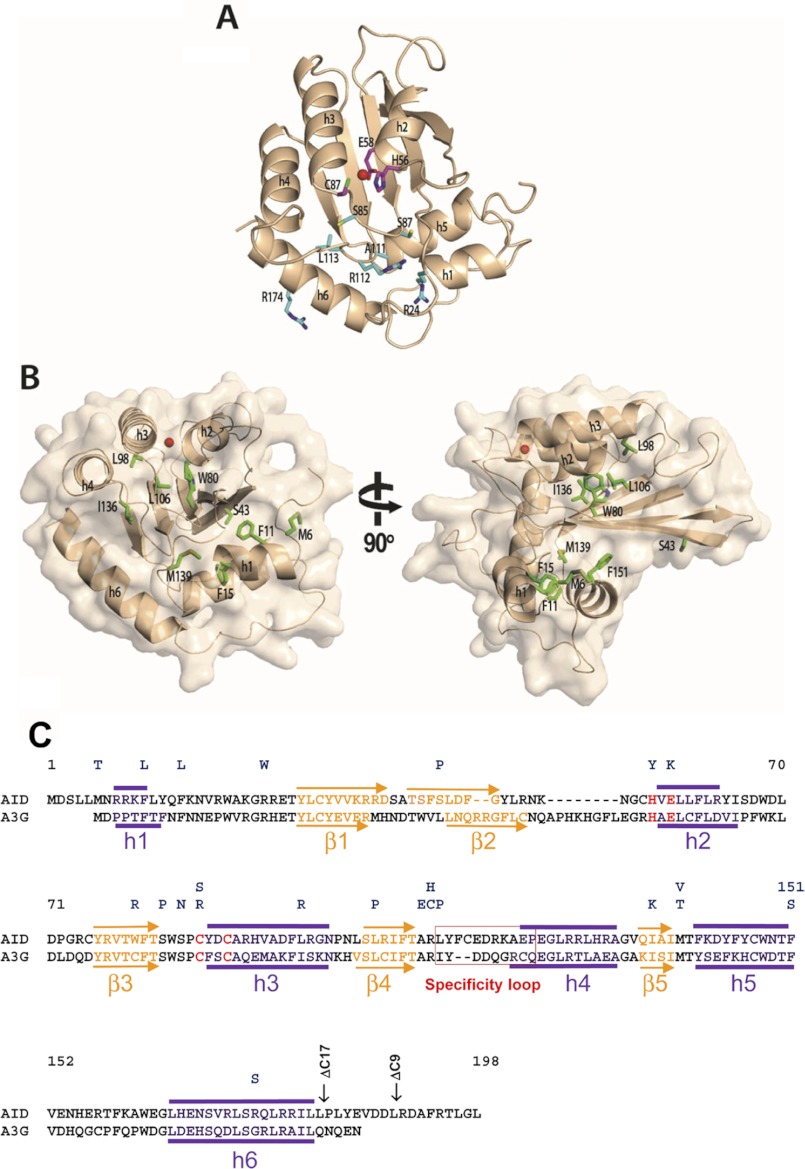
FIGURE 1.
A structural model of AID. A, AID model (wheat) was generated using Apo3G-CD2 as a template. Class I residues H56Y, E58K, and C87R/C87S (magenta sticks) are important for catalysis. His-56 and Cys-87 are involved in coordinating the zinc ion (red sphere), and Glu-58 is involved in proton shuffling. Residues in class II (R24W, S83P, S85N, A111E, R112C/R112H, L113P, and R174S, cyan sticks) are likely involved in interaction with the ssDNA substrate. B, class III residues (Met-6, Phe-11, Phe-15, Trp-80, Leu-98, Leu-106, Ile-136, Met-139, and Phe-151, green sticks) are important for maintaining the structural integrity of AID. C, alignment of AID and Apo3G-CD2. HIGM-2 base substitution mutations and C-terminal deletion mutations are indicated on top. Secondary structure predictions based on the AID model are indicated above the AID sequence. α-Helices and β-strands depicted below the A3G-CD2 sequence are from its x-ray crystal structure (17). Active site residues are highlighted in red.