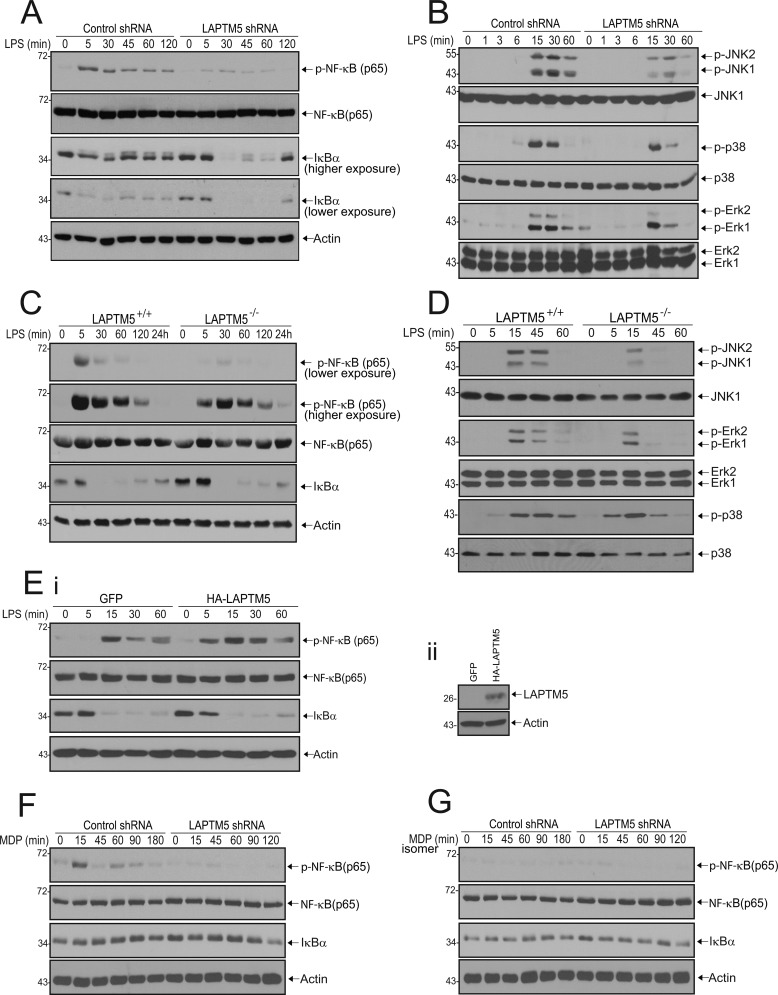
FIGURE 3.
LAPTM5 is required for TLR4 and NOD2-mediated activation of NF-κB and for TLR4-dependent MAPK signaling. A and B, knockdown of LAPTM5 leads to reduced TLR4-mediated NF-κB and MAPK activation. Stable RAW264.7 cells expressing control or LAPTM5 shRNA were stimulated with 1 μg/ml LPS for the indicated times. The cells were lysed and analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies toward phosphorylated NF-κB (p-NF-κB (p65)), NF-κB (p65), IκBα, and actin (A) and phosphorylated JNK1/2 (p-JNK1/2), p38 (p-p38), and Erk1/2 (p-Erk1/2) and the respective total levels of these downstream effectors (B). C and D, knock-out of LAPTM5 leads to reduced TLR4-dependent NF-κB and MAPK activation. BMDMs from wild-type (LAPTM5+/+) and LAPTM5 knock-out (LAPTM5−/−) mice were stimulated with 100 ng/ml LPS, lysed at the designated time points, and subjected to immunoblot analysis with antibodies as indicated in A. E, exogenous expression of LAPTM5 in LAPTM5−/− BMDMs partially rescues NF-κB activation. LAPTM5−/− BMDMs were transduced with a retrovirus expressing GFP alone (GFP) or GFP-IRES HA-tagged LAPTM5 (HA-LAPTM5). Panel i, cells were stimulated with 100 ng/ml LPS, lysed at the indicated time points, and subjected to immunoblot analysis with antibodies as indicated in A. Panel ii, expression of HA-tagged LAPTM5. The cell lysates were immunoblotted with anti-HA antibodies to detect exogenous HA-LAPTM5 or actin antibodies as a control for protein loading. F and G, LAPTM5 knockdown results in reduced NOD2-mediated NF-κB activation. Stable RAW264.7 cells expressing control or LAPTM5 shRNA were stimulated with 10 μg/ml MDP (D) or 10 μg/ml inactive MDP isomer (E). After the indicated time periods, the cells were lysed and immunoblotted as in A.