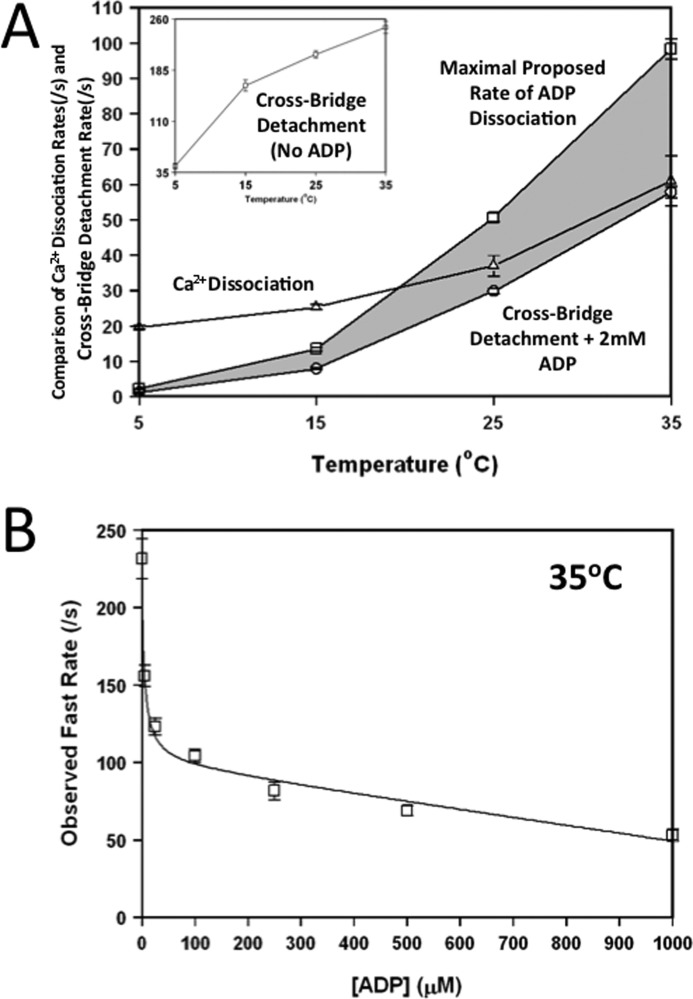
FIGURE 7.
Effect of temperature on the rates of Ca2+ dissociation and cross-bridge detachment as reported by TnC in rabbit myofibrils. Panel A shows the comparison between the rates of rigor Ca2+ dissociation (△), cross-bridge detachment + 2 mm ADP (○), and maximal proposed rate of ADP dissociation (□) at increasing temperatures (* denotes calculated value). Rigor Ca2+ dissociation (△) was determined by mixing TnCIANBDT53C myofibrils in Buffer A + 200 μm Ca2+ with an equal volume of the Buffer A + 10 mm EGTA. The Cross-Bridge Detachment (No ADP) plot (inset, □) represents cross-bridge detachment from ADP free myofibrils. Cross-bridge detachment in presence of ADP was determined by mixing TnCIANBDT53C myofibrils in Buffer A + 5 mm EGTA + 2 mm ADP (○) with an equal volume of the Buffer A + 5 mm EGTA + 2 mm ATP. The shaded area is used to highlight the difference between the maximal proposed rate of ADP dissociation to that with 2 mm ADP. Panel B shows the effect that increasing ADP had on the apparent fast rate of cross-bridge detachment of Ca2+-free TnCIANBDT53C rabbit myofibrils at 35 °C. Increasing concentrations of ADP (0–2000 μm) were added to the Ca2+-free TnCIANBDT53C myofibrils in Buffer A + 5 mm EGTA and rapidly mixed against Buffer A + 2 mm ATP at 35 °C. The concentrations of ADP shown were the final concentration after mixing in the stopped-flow.