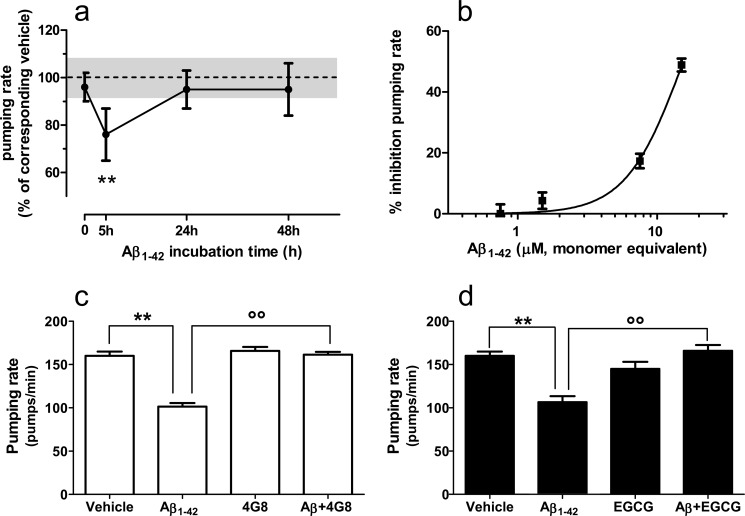
FIGURE 5.
Effects of Aβ1–42 species on pharyngeal pumping rate in C. elegans. a, synthetic Aβ1–42 (100 μm) was incubated at 25 °C and sampled at different times (t = 0, 5, and 24 h), diluted to 10 μm in PBS, and administered to N2 worms for 2 h. Control worms were fed vehicle alone (dotted line). Only the samples preincubated for 5 h (i.e., those containing the 4G8-binding Aβ1–42 oligomers) markedly inhibited the pumping rate. The values are the means ± S.E. (n = 20), expressed as a percentage of the corresponding control. **, p < 0.01 versus t = 0, Bonferroni's test after two-way ANOVA. b, dose-response effect of Aβ1–42 oligomers on pharyngeal pumping. Worms were fed Aβ1–42 (0.5–10 μm) previously incubated for 5 h. The values are the means ± S.E., expressed as percentages of control worms fed vehicle. c, the inhibitory effect of Aβ1–42 oligomers on pumping rate was antagonized by 4G8. Aβ1–42 was preincubated for 5 h, added with 4G8 (1:500, v/v in vehicle), and incubated for further 30 min before administration to worms. Control worms were fed vehicle or 4G8 alone. The values are the means ± S.E. (n = 16). Two-way ANOVA showed a significant interaction between Aβ1–42 and 4G8 (p < 0.01). **, p < 0.001 versus vehicle; °°, p < 0.001 versus Aβ1–42 (Bonferroni's test). d, EGCG antagonized the inhibitory effect of Aβ1–42 oligomers on pharyngeal pumping. Aβ1–42 (100 μm) was incubated at 25 °C with or without EGCG (100 μm). After 5 h, the samples were diluted 10 times and administered to worms. Control worms were fed vehicle or 10 μm EGCG alone. The values are the means ± S.E. (n = 16). Two-way ANOVA showed a significant interaction between Aβ1–42 and 4G8 (p < 0.01). **, p < 0.001 versus vehicle; °°, p < 0.001 versus of Aβ1–42 (Bonferroni's test).