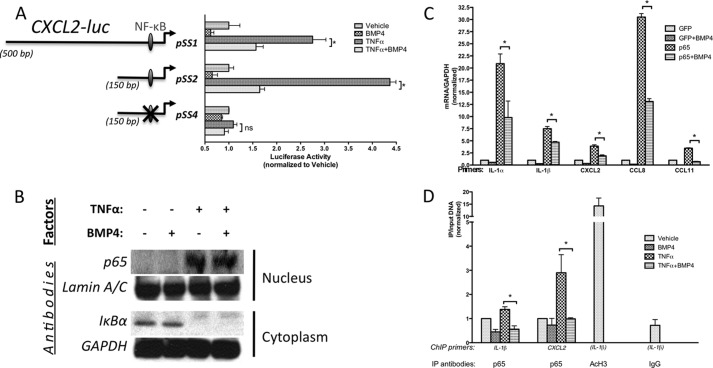
FIGURE 2.
BMP4 antagonizes the TNFα-activated NF-κB pathway. A, PAC-1 cells were transfected with wild-type (PSS1, −428/+76; PSS2, −80/+76) or mutant CXCL2 reporter constructs, which are mutated in the NF-κB binding site as indicated (PSS4, a mutation within the NF-κB site at −76/−67), treated with with or without TNFα (10 ng/ml) in the presence or absence of BMP4 (3 nm) for 18 h and followed by luciferase assay. Luciferase activities were normalized to the β-galactosidase activities. B, hPASMCs were pretreated with or without BMP4 (3 nm) for 1 h, following stimulated by TNFα (10 ng/ml) for 5 min. Nucleus was separated from cytoplasm and NF-κB p65 and IκBα expression levels were examined by immunoblot analysis. C, hPASMCs were infected with adenovirus carrying NF-κB p65 (Adeno-p65) or GFP (control) cDNA, followed by treatment with 3 nm BMP4 for 24 h, and then subjected to qRT-PCR assay. D, recruitment of NF-κB p65 to the IL-1β or CXCL2 promoter was examined by CHIP with an anti-NF-κB p65 in hPASMCs, followed by quantitative realtime-PCR analysis using primers specific for the IL-1β or CXCL2 promoter. Immunoprecipitation with AcH3 or nonspecific IgG were used as positive or negative control. Results are shown as relative enrichment of the IL-1β or CXCL2 promoter after IP and the basal level of binding without treatment was set to 1. Mean values are expressed ± S.E.