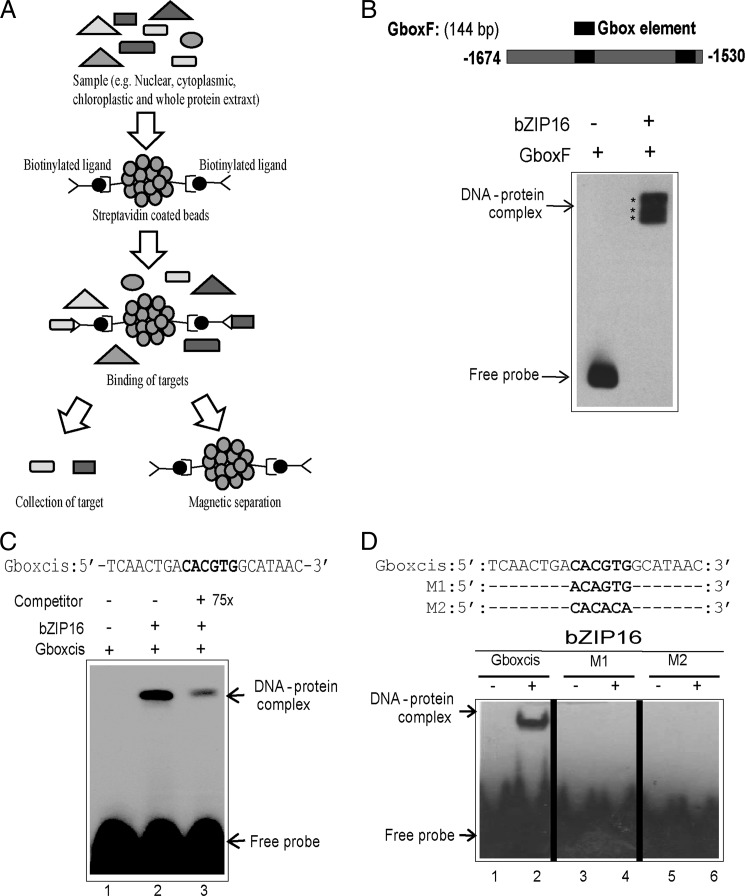
FIGURE 1.
DNA affinity trapping of AtbZIP16 using LHCB2.4 promoter. A, biotinylated ligands were immobilized on streptavidin-coated beads and mixed with samples to allow binding. Magnetic separation was used, and the target proteins were collected for subsequent analysis. B, EMSA verified binding of recombinant AtbZIP16 protein to the 144-bp fragment of the LHCB2.4 promoter containing the G-box (positions −1530 to −1674). C, EMSA with complementary synthetic oligonucleotides representing the G-box element and recombinant AtbZIP16 protein. A competition assay was performed by adding unlabeled G-box probe at 75× excess. D, sequence of complementary synthetic oligonucleotides representing the G-box and its mutagenized half-sites used with AtbZIP16 in EMSA. The biotin-labeled DNA probes were incubated in the presence (+) or absence (−) of 4 μg of recombinant AtbZIP16 protein, and the DNA-protein complexes were separated from free DNA by non-denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The signals were detected with a chemiluminescent nucleic acid detection method. Positions of free DNA and protein-DNA complexes are indicated by an arrow.