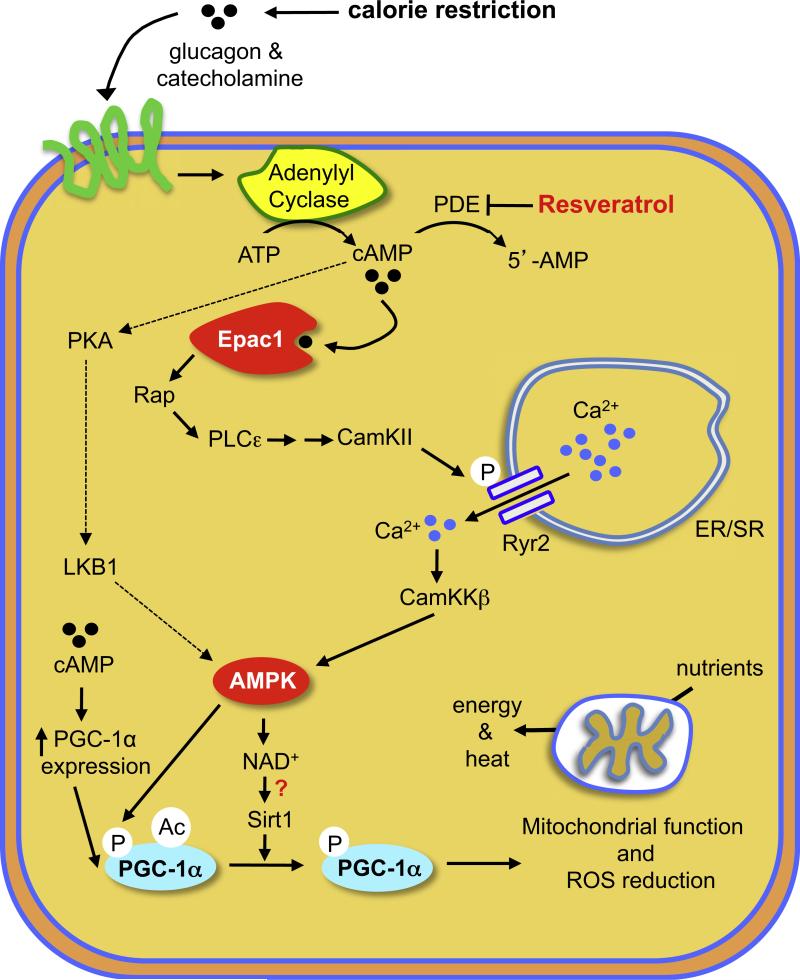
Figure 7. Proposed Model of How Resveratrol Mimics CR.
Resveratrol inhibits PDE activity and induces cAMP signaling via Epac1, which activates PLCε, resulting in Ca2+ release via the Ryr2 Ca2+ channel and, ultimately, the activation of the CamKKβ-AMPK pathway. CR increases cAMP levels by increasing glucagon and catecholamine levels, which activate AC activity and cAMP production. AMPK increases mitochondrial biogenesis and function by increasing PGC-1α expression, NAD+ levels, and Sirt1 activity. An additional pathway that may contribute to resveratrol action is indicated with dotted lines.