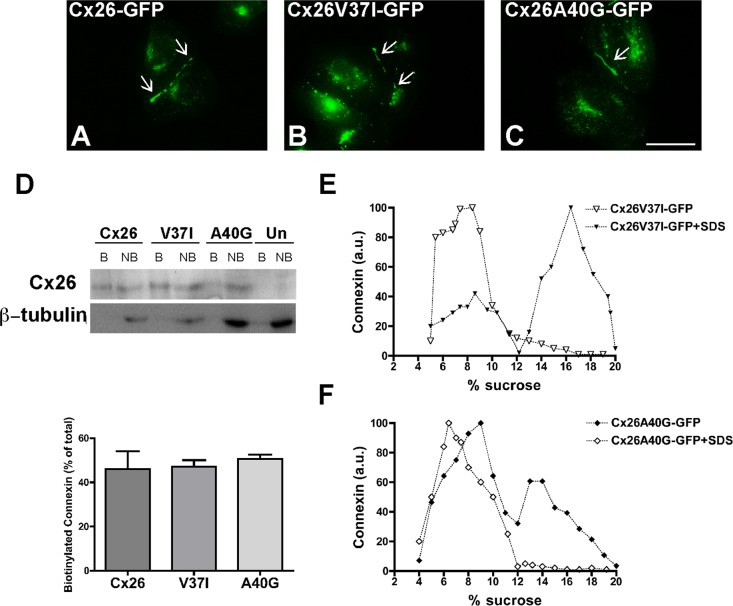
FIGURE 3:
The deafness-associated Cx26 mutants, Cx26V37I, and Cx26A40G, oligomerized and formed gap junction plaques and hemichannels in the plasma membrane. (A–C) Photomicrographs show the distribution of fluorescence in HeLa cells transfected with Cx26-GFP (A), Cx26V37I-GFP (B), or Cx26A40G-GFP (C). Arrows point to gap junction plaques. Scale bar: 15 μm. (D) Immunoblot of streptavidin-bound (“B”) and not bound (“NB”) proteins after cell surface biotinylation of HeLa cells transiently transfected with Cx26-GFP, Cx26V37I-GFP, or Cx26A40G-GFP using anti-GFP (top) or anti–β-tubulin (bottom) antibodies. The absence of a β-tubulin band in the bound (biotinylated) fractions confirms the integrity of the plasma membrane during cell surface biotinylation. Graph illustrates the quantification of the immunoblot data. Bars represent the percentage of the total protein that was biotinylated (average + SEM; n = 3). (E and F) Graphs represent the levels of Cx26V37I-GFP (E) and Cx26A40G-GFP (F) in sucrose gradient fractions detected by immunoblotting using anti-Cx26 antibodies. Triton X-100–soluble extracts from HeLaCx26V37I-GFP or HeLaCx26A40G-GFP cells treated with SDS (open symbols) or left untreated (closed symbols) were subjected to sedimentation velocity through 5–20% sucrose gradients.