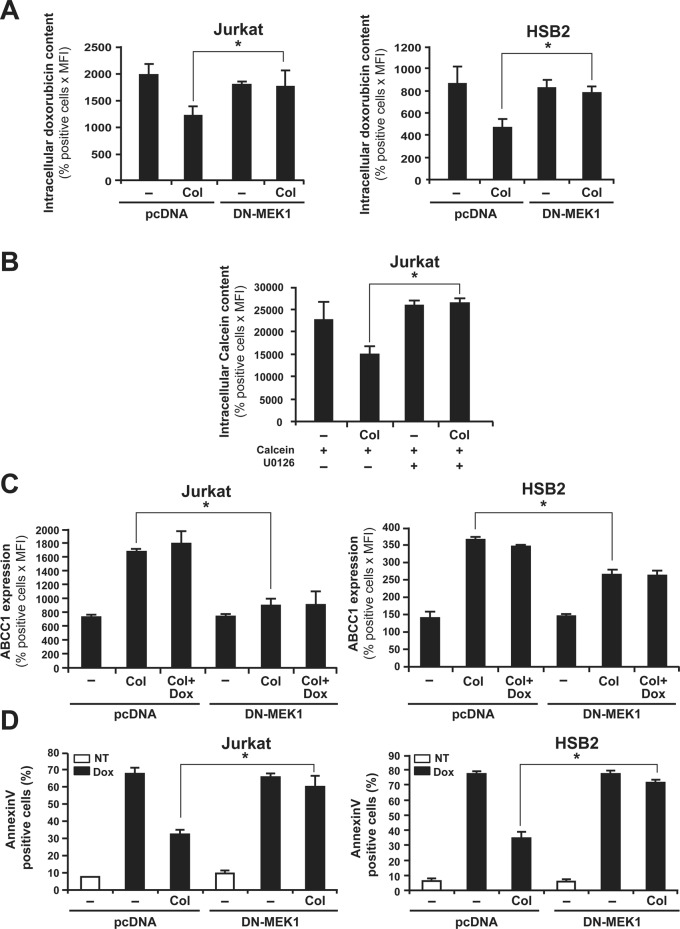
FIGURE 8:
ERK inhibition abrogates collagen-induced drug efflux, ABCC1 expression, and resistance against doxorubicin-mediated apoptosis. (A) DN-MEK-1 inhibits the ability of collagen to reduce intracellular doxorubicin content. Cells were transfected with DN-MEK1 or pcDNA (empty plasmid). After transfection, the cells were activated or not with collagen (Col) and then treated with doxorubicin. The intracellular doxorubicin content was measured by flow cytometry. (B) The MEK-1 inhibitor abrogates collagen-mediated calcein efflux. Jurkat cells were preincubated or not for 1 h with 10 μM of the MEK/ERK inhibitor (U0126) before their activation or not with collagen (Col) and treatment with calcein-AM. Intracellular calcein content was then assessed by flow cytometry. (C) DN-MEK-1 abolishes the up-regulation of ABCC1 expression levels by collagen. Expression of ABCC1 in transfected cells was determined by ABCC1 staining and flow cytometry analysis as described in Materials and Methods. (D) DN-MEK-1 abolishes the protective effect of collagen on doxorubicin-induced apoptosis. Transfected cells were activated or not with collagen and then treated or not with doxorubicin (Dox) for 16 h (NT, nontreated). Apoptosis was determined by annexin V staining and flow cytometry analysis. The results represent mean values ± SD from three independent experiments. *p < 0.05 where indicated.