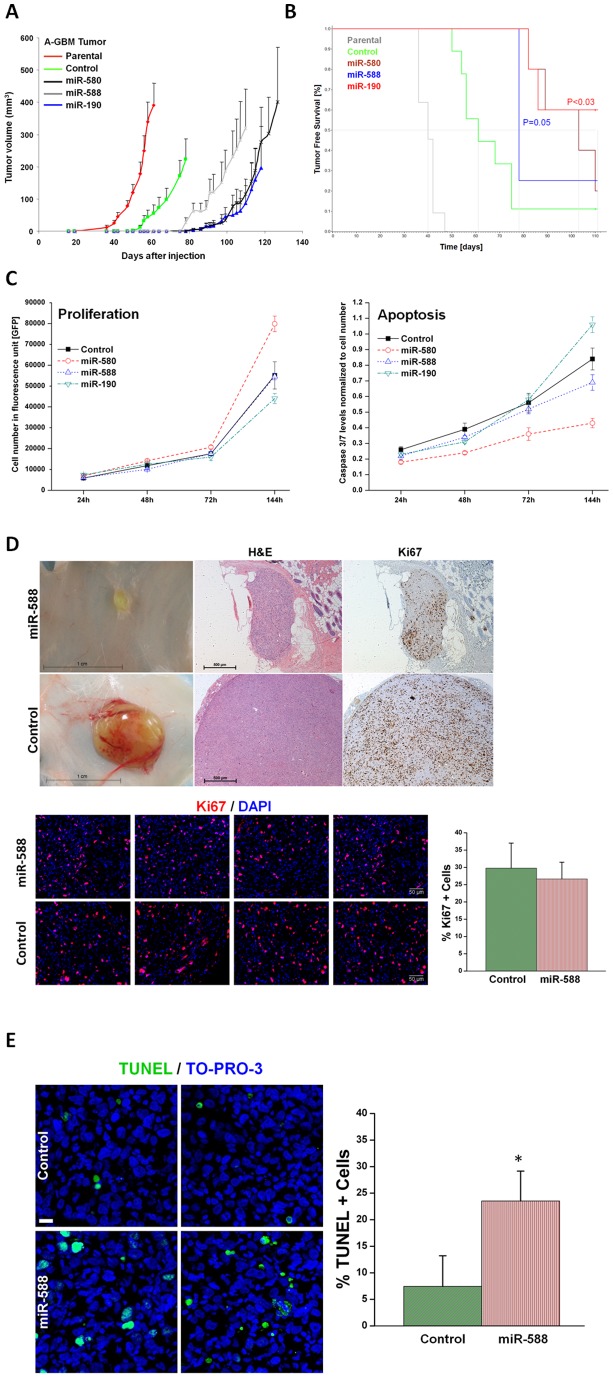
Figure 2. Over-expression of DmiRs reversed tumor phenotype.
Tumor growth kinetics of angiogenic fast-growing glioblastoma cells (A-GBM) was monitored in-vivo (A). Average tumor volume of parental tumor (labeled in red line) n = 11, cells infected with GFP only control vector (n = 9), miR-580 (n = 5), miR-588 (n = 4), and miR-190 (n = 5) expressing A-GBM tumors. Kaplan-Meier analysis of tumor free survival (B). The criterion for “tumor free” was defined as mice bearing no detectable tumors by gross examination or tumors with volume smaller than 50 mm3. The median tumor free survival was markedly increased in miR-580 and miR-588 expressing tumors as compared to the GFP control. 60% of miR-190 expressing tumors remained dormant for the whole observation period. Statistical significance was reached for miR-190 (p<0.03) and miR-580 (p = 0.05), respectively, by log-rank test. The dormancy promoting effect of DmiRs was not attributed to impaired proliferation kinetic or enhanced apoptosis of DmiR expressing tumor cells in-vitro (C). In contrast, there was a trend towards higher proliferation rates and reduced apoptosis in miR-580 expressing cells (C). Proliferating tumor cells were also detected by Ki67 immunohistochemistry and representative photomicrographs are shown (D) in dormant miR-588 expressing GBMs (107days post implantation) and fast-growing GFP expressing control tumors (day 113 after implantation). In-vivo proliferation index was determined by counting the fraction of Ki67+ tumor cells. This analysis revealed no significant difference between the dormant miR-588 and the fast growing control (GFP) tumors (p = 0.12). Enhanced apoptosis was detected in-vivo in miR-588 vs. control (GFP) tumors by TUNEL staining (E). A threefold increase in the fraction of TUNEL+ apoptotic tumor cells was found in dormant miR-588 expressing- vs. control tumors (* p<0.0001).