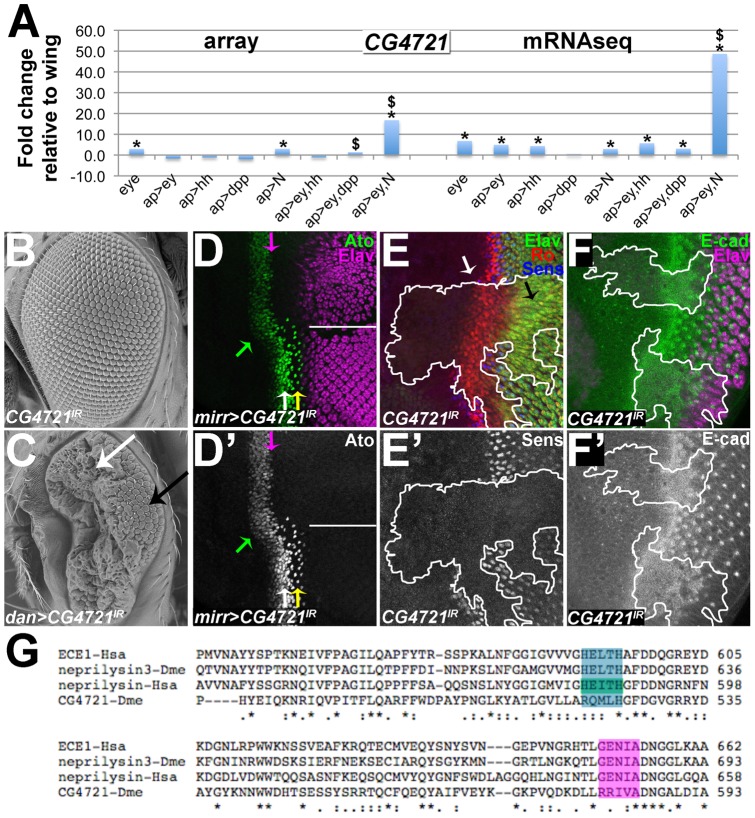
Figure 6. CG4721 encodes a neprilysin that is required for eye development.
(A) Graph showing fold-changes in CG4721 levels in the indicated genotypes. “*”indicates significant upregulation; “$” indicates signficant upregulation in ap>ey+N factor versus both ap>ey and ap>N. (B,C) Scanning electron micrographs of adult eyes of the indicated genotypes. (D) Projection of confocal sections of mirr>CG4721IR eye-antennal discs stained for anti-Ato and anti-Elav. White line divides dorsal (top) from ventral (bottom). (E,F) Projection of confocal sections of eye-antennal discs containing clones expressing CG4721IR (outline of clones marked by white lines). (E) CG4721IR tissue fails to develop R8s (marked by Sens expression). Instead, all CG4721IR cells behind the furrow express Ro and develop as R2/R5 photoreceptors (marked by Ro and Elav). (F) E-cad, which marks the furrow in wild-type tissue, is expressed in a broader domain in CG4721IR tissue compared to surrounding wild-type tissue. (G) Alignment of the catalytic domain of the predicted CG4721 protein sequence with the catalytic domain of other neprilysins from Drosophila melanogaster and Homo sapiens. Colored boxes indicate residues critical for catalytic activity.