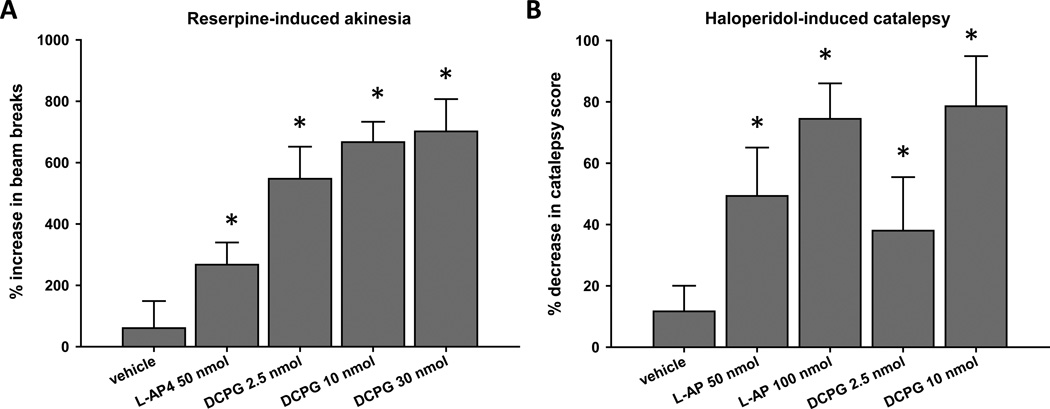
Figure 2. DCPG reverses prolonged reserpine-induced akinesia and haloperidol-induced catalepsy.
Animals were pretreated with reserpine (5 mg/kg, sc) for 18–20 hours prior to baseline locomotor activity measurement for 30 minutes (A), or with three injections of haloperidol (1.5 mg/kg, ip) evenly spaced over 18–20 hours prior to baseline catalepsy measurement (B). After baseline measurements, animals received an icv infusion of L-AP4 (50 or 100 nmol/2.5 µl), DCPG (2.5, 10, or 30 nmol/2.5 µl) or vehicle (ACSF, 2.5 µl). Five minutes after completion of infusion, locomotor activity (A) or catalepsy (B) was measured again, and the percent change from baseline measurement was calculated. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. Results were obtained from ten animals per treatment group. *P < 0.05, Dunnett’s comparison with vehicle group.