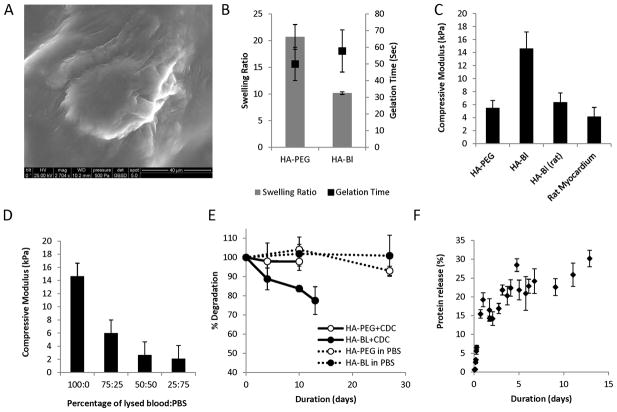
Figure 1. Characterization of HA-blood (human, lysed) and HA-PEG hydrogels.
A. Scanning electron microscopy image of CDC encapsulated in HA-blood hydrogel. (Calibration bar is 40μm).
B. Gelation time of HA-PEG and HA blood hydrogels was similar but equilibrium swelling ratio of HA-PEG hydrogels was greater than HA-blood hydrogels
C. Young’s moduli of HA-blood hydrogels using human blood was higher than the modulus of rat myocardium and HA-blood hydrogels composed of lysed rat blood (WK rats)
D. Young’s moduli of HA-blood hydrogels decreased proportionately as the concentration of lysed blood in the hydrogels decreased by diluting with PBS
E. Minimal degradation of HA-blood and HA-PEG hydrogels by hydrolysis (dashed lines). Presence of CDCs accelerates degradation of HA-blood hydrogels (solid lines).
F. Protein release from HA-blood hydrogels in PBS