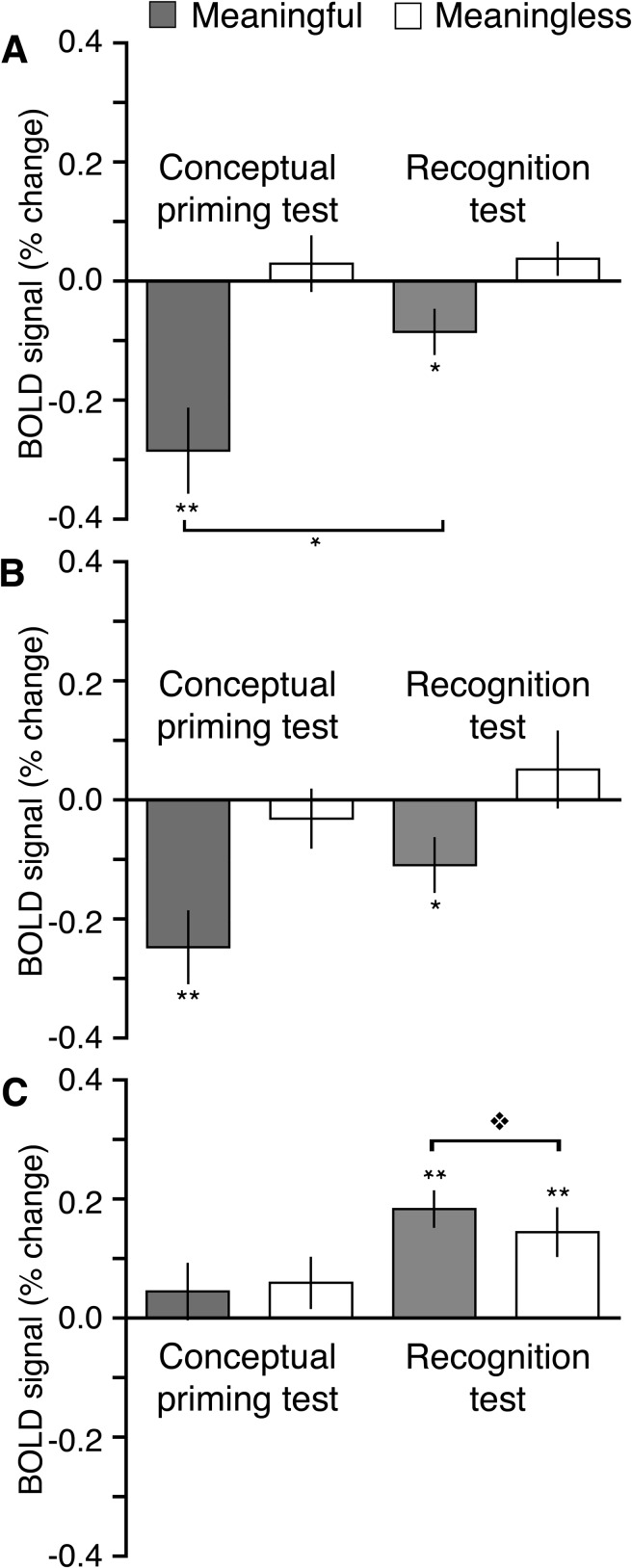
Figure 5.
Functional dissociation of brain regions sensitive to conceptual priming versus recognition. Differences in estimated activity between old and new squiggles (i.e., repetition effects, old–new) are shown separately for the meaningful and meaningless categories averaged over all regions found to be sensitive to either conceptual priming or to recognition in aforementioned analyses. (A) Repetition effects in the a priori defined conceptual ROIs shown in Figure 3. (B) Repetition effects in the regions identified as selective for conceptual priming via the double subtraction of meaningful and meaningless repetition effects shown in Figure 4A,B. (C) Repetition effects in the regions identified as selective for recognition memory judgments shown in Figure 4C,D. Error bars indicate SE. **P < 0.01. *P < 0.05.  P = 0.06.
P = 0.06.