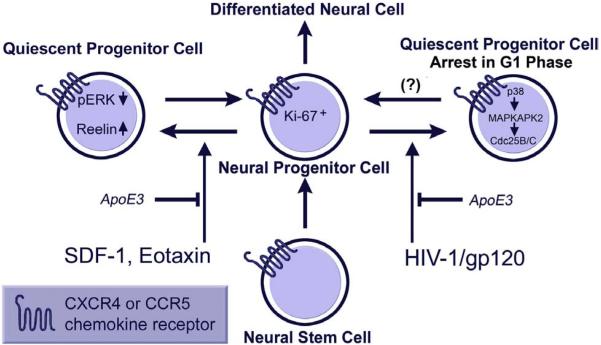
Figure 2.
Current model of HIV-1 interference with the function of neural progenitor cells and potential sites for therapeutic intervention (protective factors are shown in italic): Exposure to chemokines, SDF-1 and Eotaxin, or HIV-1/gp120 of mouse or human neural progenitor cells (NPCs) reduces proliferation and promotes quiescence. ApoE3 inhibits these effects on NPCs. NPCs express nestin and show decreased proliferation as judged by decreased BrdU incorporation. However, NPCs do not undergo apoptosis, as evidenced by lack of TUNEL staining and nuclear condensation under the same conditions (16,20,116). HIV/gp120 impairs proliferation of progenitors through activation of a pathway consisting of p38MAPK, MAPK-activated protein kinase 2 and Cdc25B/C which results in cell-cycle arrest in the G1 phase. It is not clear yet in how far this effect is reversible. Modified from (117).