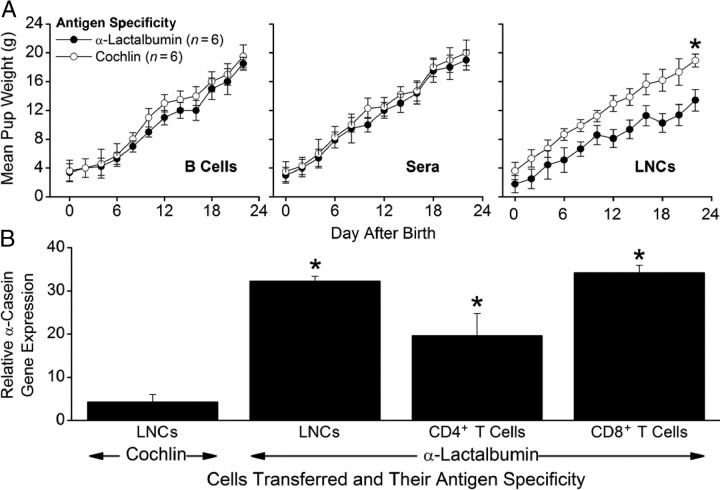
Figure 5.
Passive transfer of autoimmune breast failure with primed T cells. Lactating female SWXJ mice were injected i.p. with LNCs, CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, B cells, or sera from mice immunized previously with either recombinant α-lactalbumin or recombinant cochlin in CFA. After weaning (approximately 3 to 4 weeks after transfer), mice were euthanized for molecular analysis of tissues. A: Inhibition of growth did not occur in pups from mothers that received B cells (P > 0.50; left panel) or sera (P > 0.60; middle panel) from α-lactalbumin–immunized mice but did occur in pups from mothers that received α-lactalbumin–activated LNCs (P < 0.04; right panel). B: Significantly elevated α-casein gene expression, a surrogate marker for breast failure, did not occur in lactating breast tissues from control females receiving cochlin-activated LNCs (P > 0.10) but did occur in lactating breast tissues from females receiving α-lactalbumin–activated LNCs (P = 0.02), CD4+ T cells (P = 0.03), or CD8+ T cells (P = 0.02). Data are given as mean ± SE. Asterisks indicate significance. In all experiments, n = 6.