Figure 1.
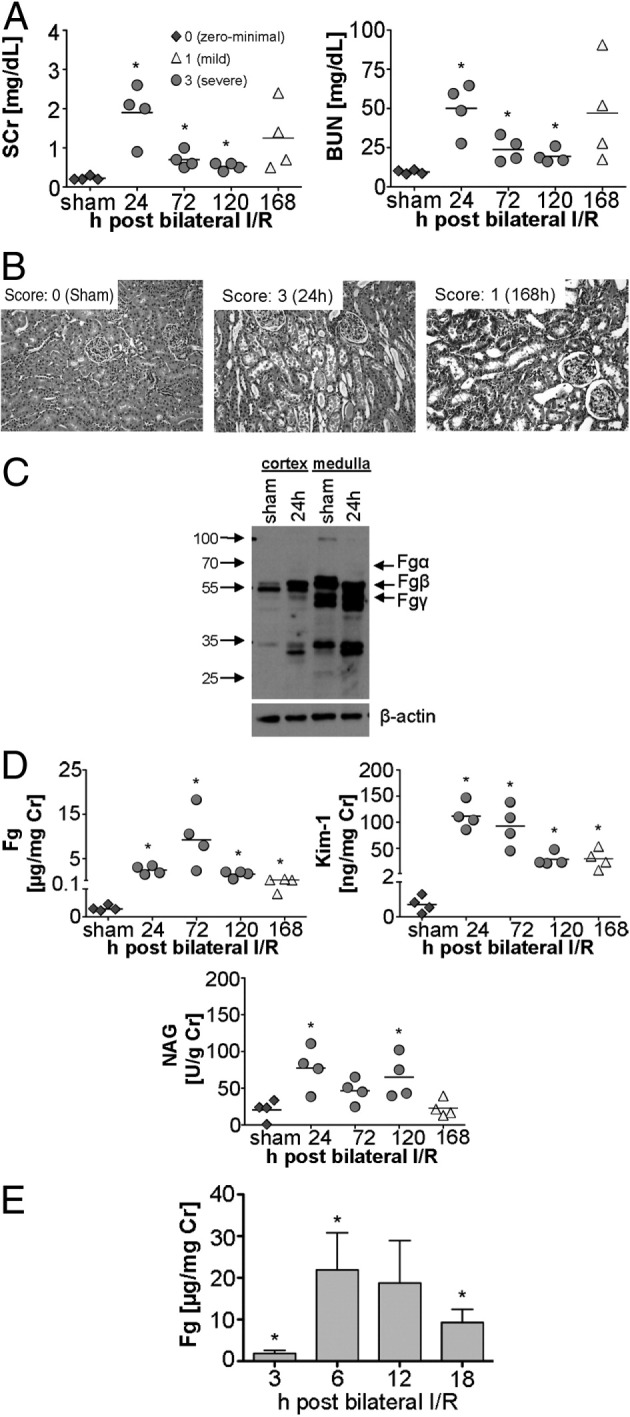
Urinary Fg increases significantly in rats after 30 minutes of bilateral renal I/R injury, correlating with the progression and resolution of AKI. A: Kidney injury parameters SCr and BUN were measured in the plasma of male Wistar rats after 30-minute bilateral renal I/R. B: Representative images of formalin-fixed, H&E-stained kidney histology sections of sham-treated versus injured tissue after 24 and 168 hours of reperfusion (n = 4 per group) show different levels of acute tubular injury. Scoring from 0 (no lesions) to 3 (severe acute tubular injury) is as described under Materials and Methods. C: Western blot analyses for Fg in rat kidney cortex and medulla collected at 24 hours after sham surgery or I/R injury revealed increased immunoreactivity of Fg- and fibrin-derived peptides in cortex and medulla at 24 hours after I/R injury, compared with sham surgery. D: Urinary levels of Fg, KIM-1, and NAG normalized to urinary creatinine over time after I/R injury. Each data point represents an induvidual animal. Colors and symbols indicate histopathology scores of acute kidney injury in the kidney. A black line indicates the mean. E: Urinary Fg levels at early time points (3, 6, 12, and 18 hours) after I/R injury. Data are indicated as mean ± SEM *P < 0.05 Student's t-test. n = 4 per group.
