Figure 3.
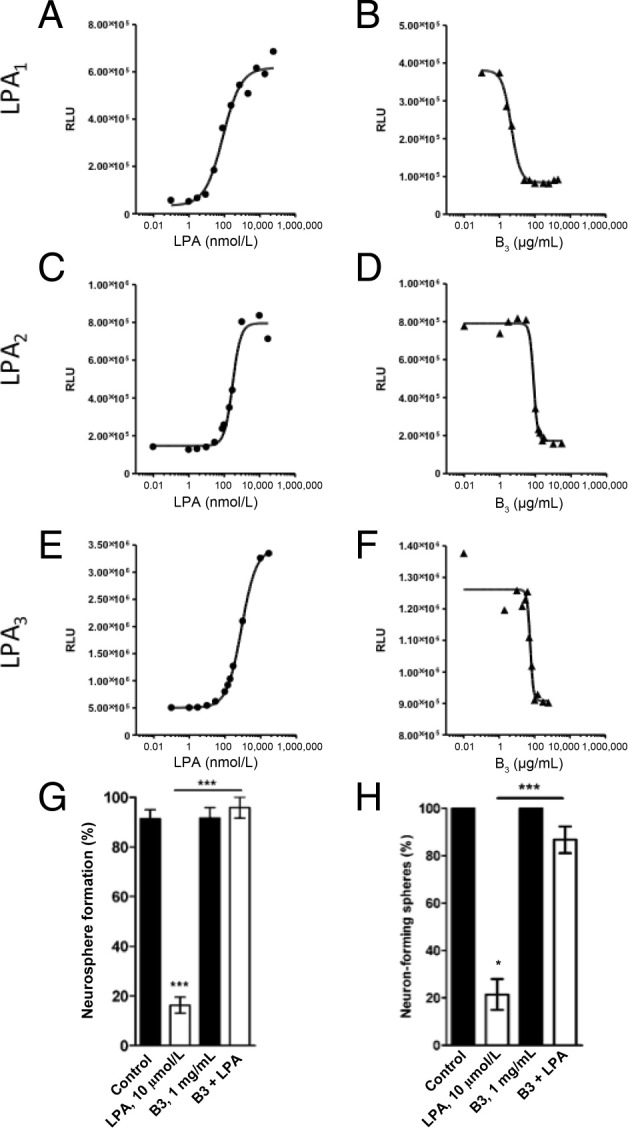
Anti-LPA mAb (B3) blocks LPA signaling in LPA1, 2, or 3 overexpressing CHO-K1 cells and in human NS/PCs. LPA activates signaling via LPA receptors LPA1 (A), LPA2 (C), or LPA3 (E). CHO-K1 cells were plated at 2.0 × 104 cells per well and were incubated at 37°C/5% CO2. After 24 hours, plates were starved with reduced serum media at 37°C for another 24 hours. The LPA standard curve was prepared by titrating 18:2 LPA (0 to 10 μmol/L) in media containing 1 mg/mL of BSA onto the plate and was analyzed as described in Materials and Methods. B, D, and F: B3 blocks LPA signaling by inhibiting LPA binding to it receptors. Media containing 200 nmol/L (for LPA1/EDG2) or 400 nmol/L (for LPA2/EDG4 and LPA3/EDG7) 18:2 LPA and increasing concentrations of B3 antibody (0 to 2000 μg/mL) were added to the corresponding CHO-K1 cells (B, D, and F, respectively) and processed as described for the LPA signaling experiment. RLU, relative light unit. Frequency of neurosphere formation (G) and neuronal differentiation (neuron-forming neurospheres) (H) in the presence or absence (control) of LPA (10 μmol/L) and/or B3 (1 mg/mL). Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM from at least three independent experiments. ***P < 0.001 by one-way analysis of variance followed by the Tukey test, α = 0.001.
