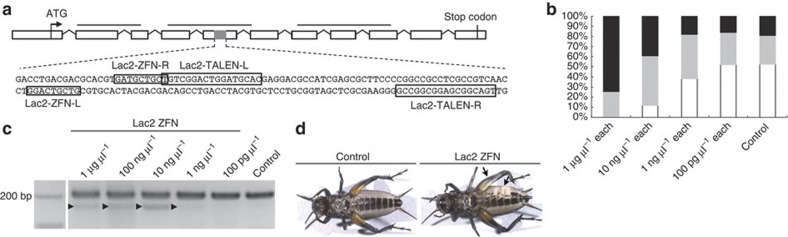
Figure 2. Design and application of ZFNs and TALENs targeted to Gb′lac2.
(a) Structure of the Gb′lac2 gene, with open boxes representing exons mapped on the Gryllus genomic sequence. Black bars indicate Cu-oxidase domains 1–3. The grey region of the fifth exon is expanded to provide the gene sequence that includes the 9 or 17 bp ZFN and TALEN binding sites, respectively (shown in boxes). (b) Dose-dependent toxicity of Gb′lac2 ZFN mRNAs in cricket embryos. The percentages of dead (black), deformed (grey) and normal (white) embryos at 2 days postinjection are shown. The control was embryos injected with Lac2-L ZFN mRNA alone. The percentage of embryos that developed normally increased with decreasing concentrations of Gb′lac2 ZFN mRNAs (0/43 for 1 μg μl−1 each, 6/51 for 10 ng μl−1 each, 19/50 for 1 ng μl−1 each, 13/25 for 100 pg μl−1 each and 11/21 for control). (c) Using a Surveyor nuclease assay, mutations in Gb′lac2 were detected following the microinjection of crickets with Gb′lac2 ZFN mRNAs. Products cleaved by Surveyor nuclease (indicated with arrowheads) were detected at 1 μg μl−1, 100 ng μl−1, 10 ng μl−1 and 1 ng μl−1 of Lac2 ZFN injected. (d) Imaging of control and Gb′lac2 ZFN final-instar nymphs. Mutagenesis of somatic cells in G0 crickets was detected based on the presence of a white spot phenotype by epidermal cells (indicated with arrows).