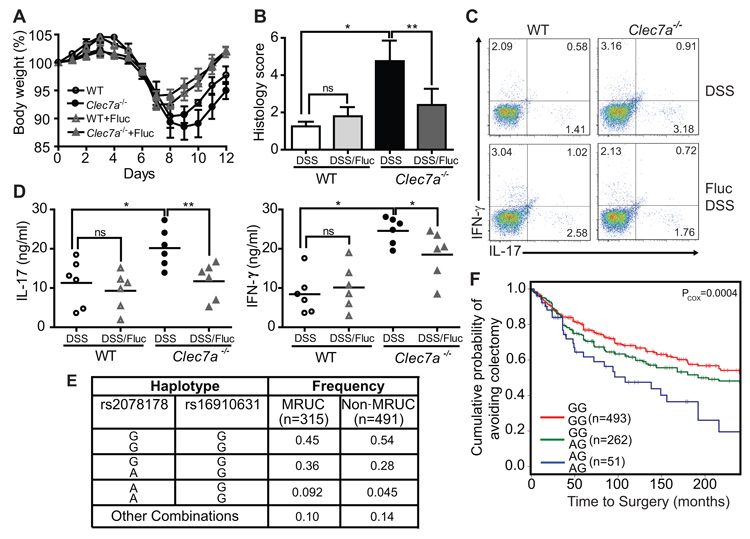
Figure 4. Anti-fungal therapy ameliorates colitis in Clec7a−/− mice and CLEC7A associates with ulcerative colitis severity in humans.
(A) WT and Clec7a−/− mice were given fluconazole in their drinking water for total of 14 days (starting 2 days prior the induction of DSS colitis), and body weight was measured. Weight loss is shown in (A) (p<0.05). Histology score (B), the percentage of IL-17 and IFN-γ producing CD4+ T cells in LI-LP (C), and IL-17 and IFN-γ production in MLNs (D) were determined 4 days after the 7 days of DSS treatment. Each symbol represents a different mouse. One of three independent experiments with similar results is shown. Error bars, s.d., * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01. (E) Specific CLEC7A haplotypes associate with medically refractory ulcerative colitis (MRUC). Haplotypes were formed from rs2078178 and rs16910631 using PHASE v2.3. Haplotypes listed as “Other Combinations” were those that could not be reliably determined (posterior p<0.95). (F) The CLEC7A “AG/AG” haplotype associates with severity of disease as indicated by earlier progression to colectomy. Haplotypes were tested for association with time to surgery by fitting the MRUC/non-MRUC and time to surgery with a Cox proportional hazards model.