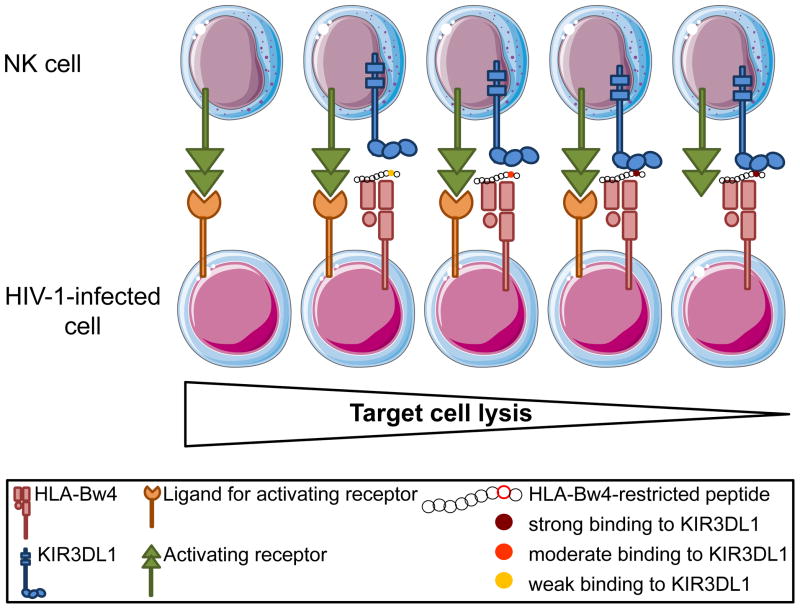
Figure 2. Influence of the presented peptide on KIR3DL1-HLA-Bw4 interaction and NK cell activation.
Single amino acid changes in the C-terminus of the peptide presented by HLA-Bw4 can significantly impact KIR3DL1-HLA-Bw4 interactions, and therefore NK cell function. Presentation of an endogenous or a viral peptide that can bind to KIR3DL1 with a high affinity might result in a strong inhibitory signal to NK cells. In such cases, NK cell activation, and potentially killing of a target cell, might only occur in the presence of strong concomitant activating signals delivered via other NK cell receptors. In contrast, mutations leading to a weaker binding between KIR3DL1 and its HLA-Bw4 ligand might lower the threshold of NK cell activation and favor target cell lysis.