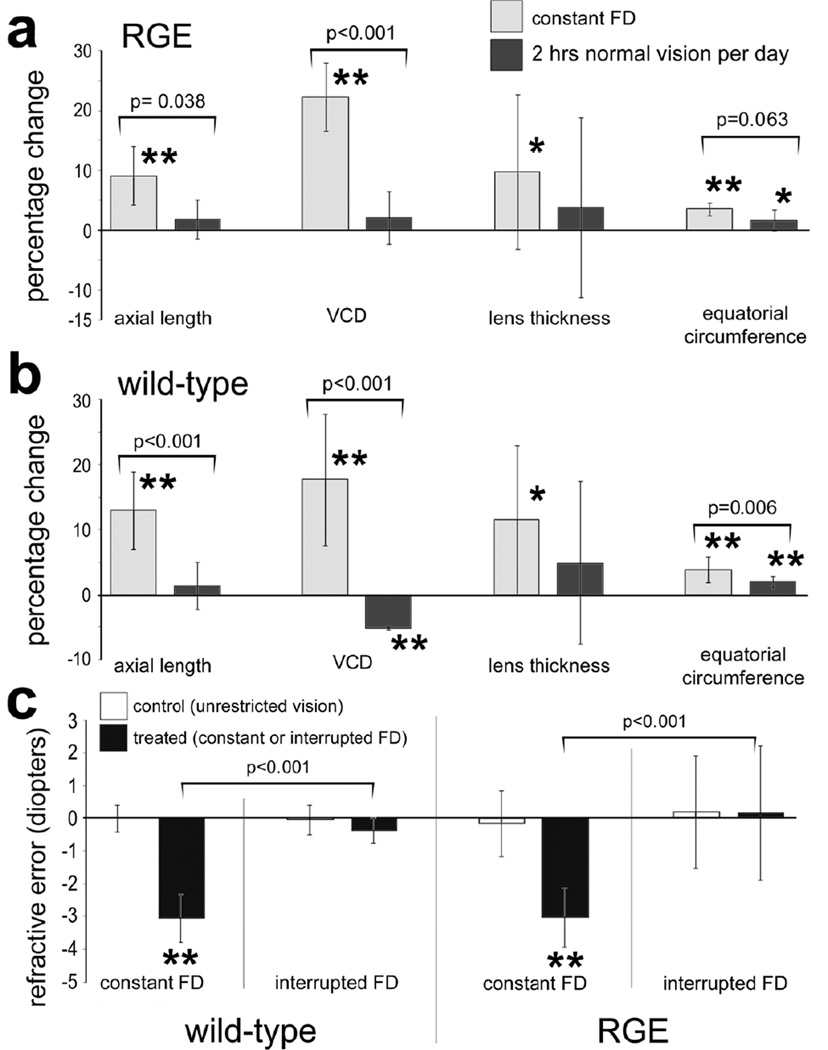
Figure 3.
Brief daily periods of unobstructed vision interrupting FD prevent ocular enlargement and myopia in WT and RGE chicks. Measurements of axial length, vitreous chamber depth (VCD), lens thickness, and equatorial circumference were calculated as percentage change relative to contralateral control eyes (a and b). The mean refractive error for treated and control eyes was determined for each experimental condition; WT constant FD, WT interruption of FD, RGE constant FD and RGE interruption of FD. Significance of difference in percentage change or between control and treated eyes within a treatment group was determined by using a paired two tailed Student’s t-test (*p<0.05; **p<0.001). Significance of difference between treatment groups was determined by using a one-way ANOVA (p≤0.002) and a post-hoc Bonferroni analysis. Error bars represent standard deviation. Asterisks indicate significant differences within a treatment group (percent change), and brackets and p-values indicate significant differences between treatment groups (constant FD vs interrupted FD).