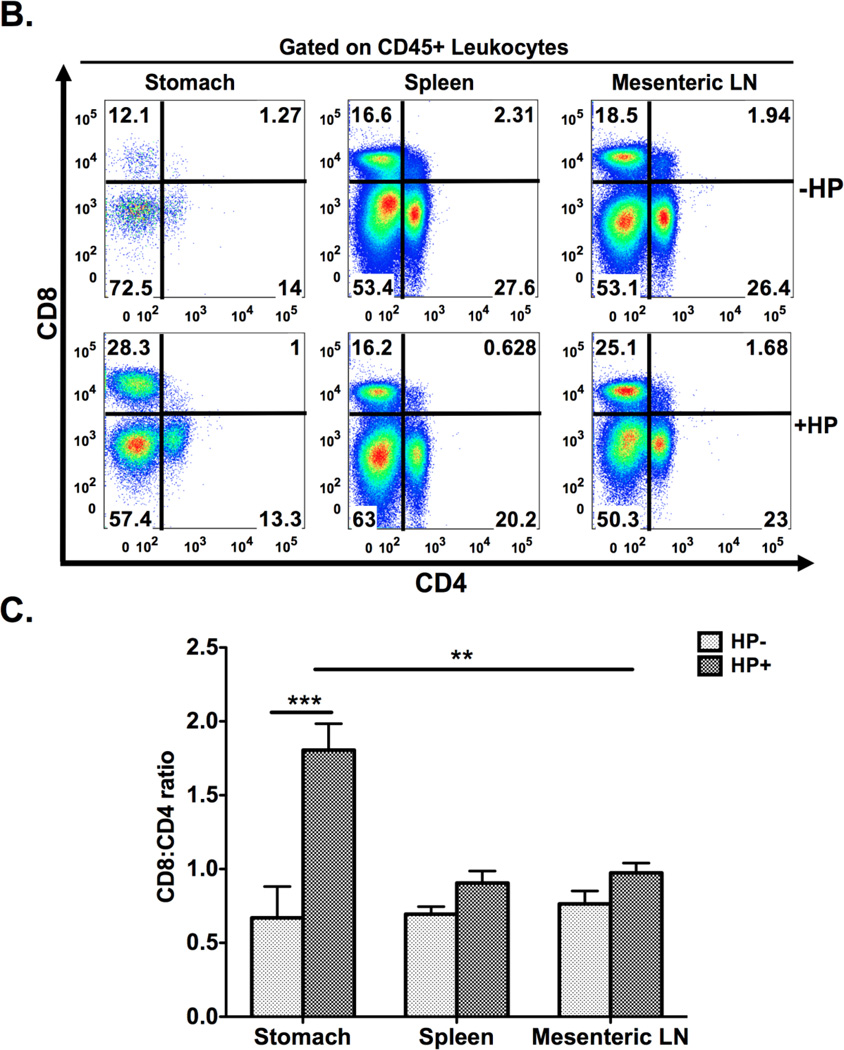
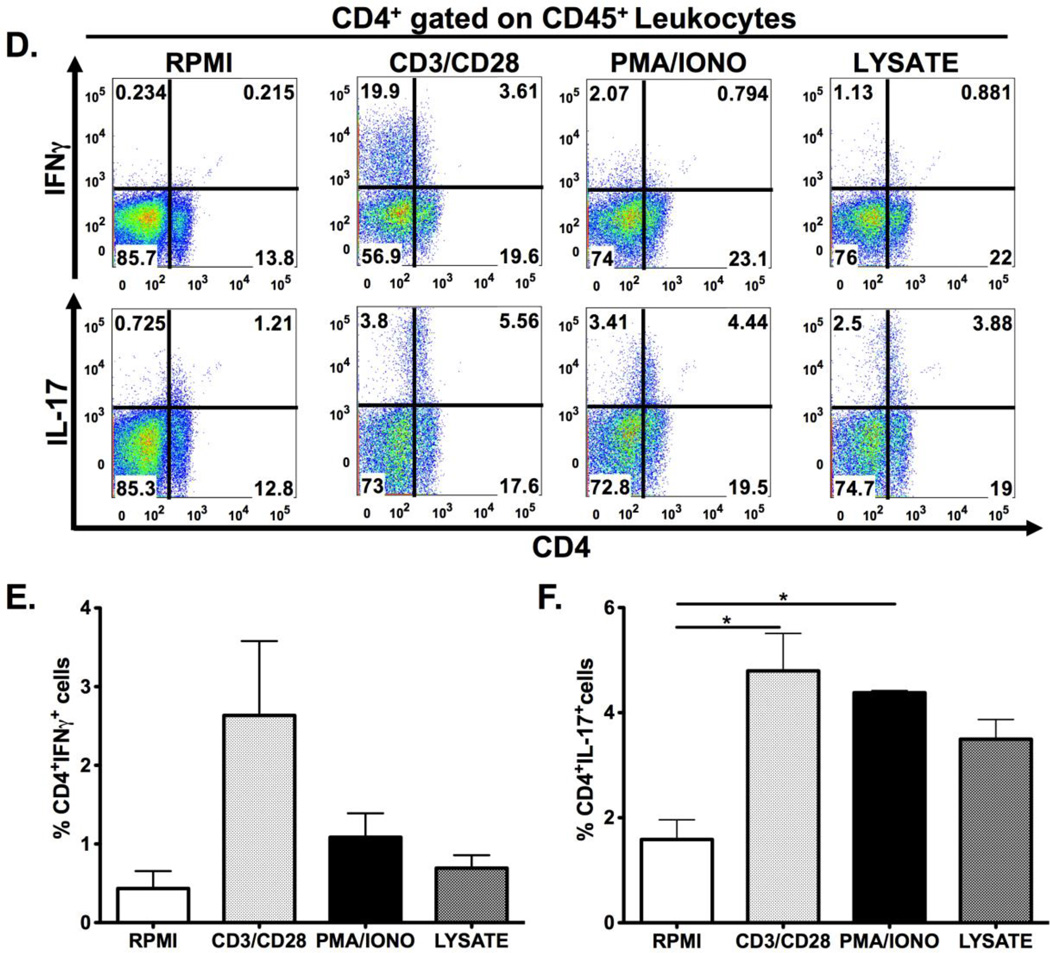
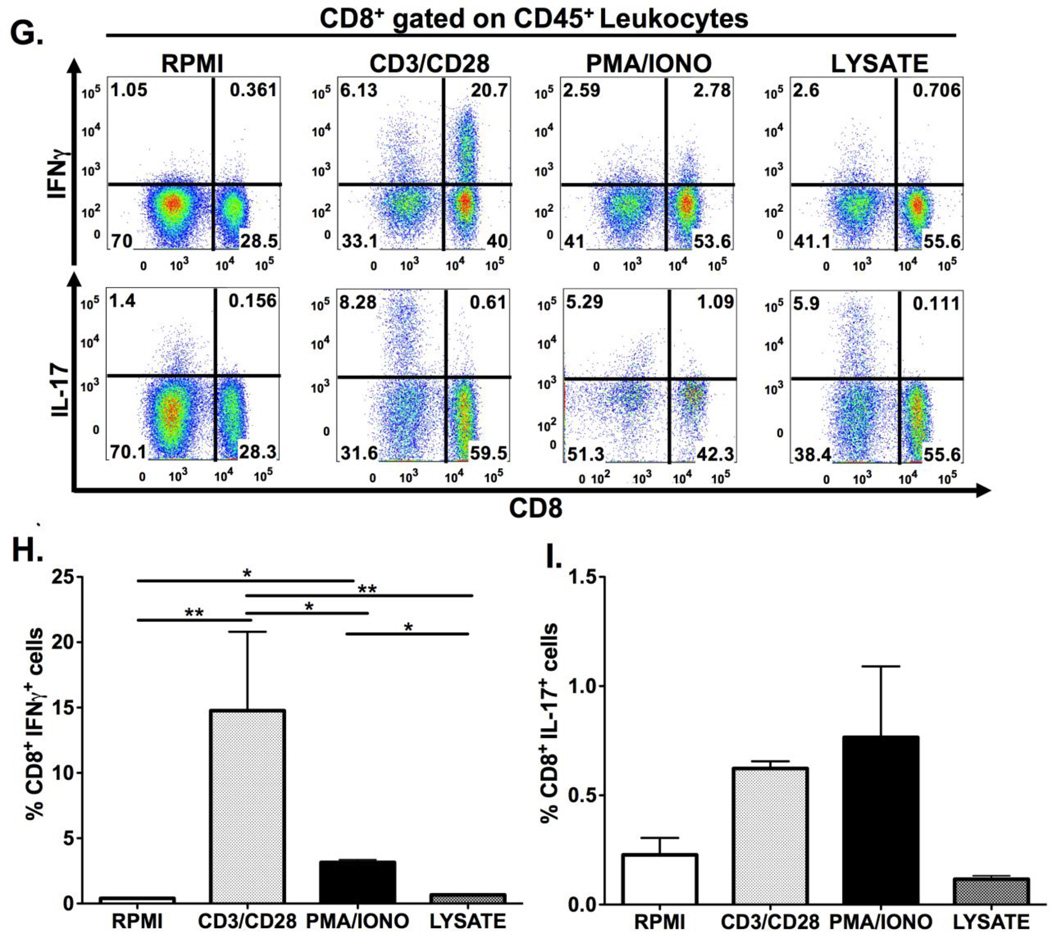
Figure 2. Schematic diagram of gastric isolation protocol (A) and immunophenotyping gastric CD4+ and CD8+ subsets during H. pylori infection. (B–I).
Infection with H. pylori (HP) strain PMSS1 increases the ratio of CD8+ to CD4+ lymphocytes altered within the gastric compartment (B, C). To phenotype CD4+ and CD8+ subsets, gastric lymphocytes were cultured with CD3/CD28, PMA/IONO and H. pylori lysate or RPMI as a control. CD4+ lymphocytes produce IL-17A with CD3/CD28, PMA/IONO and lysate stimulation. (D–F) IFNγ production is highest in CD4+ lymphocytes after CD3/CD28 stimulation. For CD8+ lymphocytes, IFNγ is significantly higher after CD3/CD28 stimulation compared to PMA/Ionomycin and lysate conditions. IL-17A expression is evident in a small percentage of CD4+ and, to a lesser extent, CD8+ cells after either indirect or direct stimulation. (G–I) Graphs represent the mean ± standard error of 4 mice pooled per experiment; results representative of 3 independent experiments. Groups were compared using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed post-hoc by Tukey multiple comparison tests on log-transformed data. Significant differences are represented by the following *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.