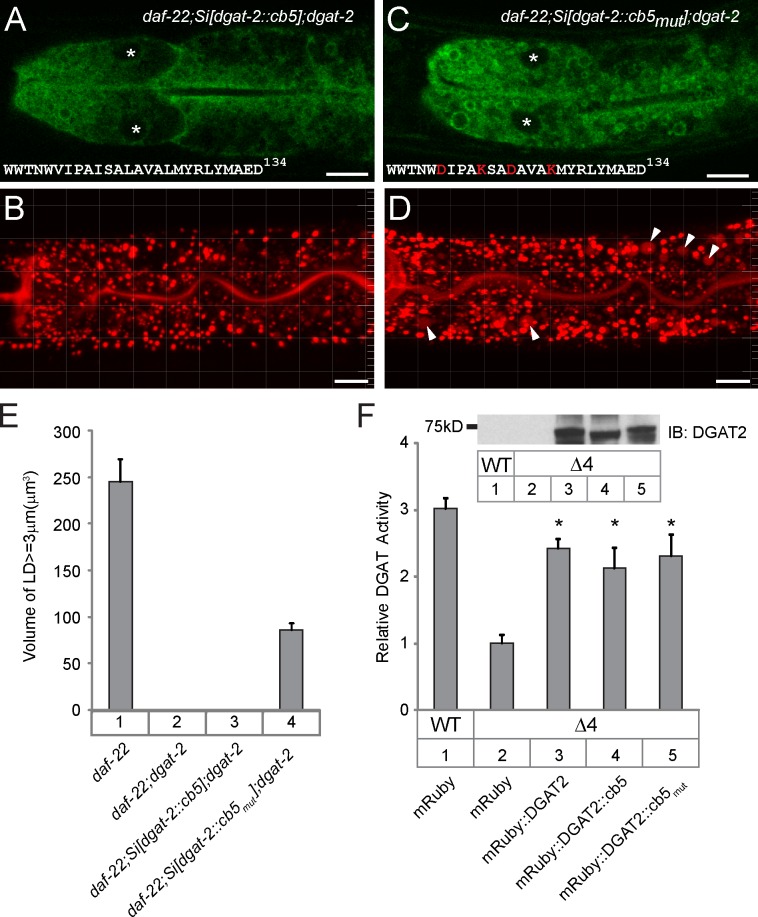
Figure 7.
LD targeting of DGAT-2 is critical for its function. (A and B) The single-copy transgene hjSi76[vha-6p::gfp::dgat-2::cb5] expressed the ER-tethered GFP::DGAT-2::cb5 fusion protein at physiological levels and failed to restore LD expansion in daf-22(ok693); dgat-2(hj44) mutant animals. (A) A representative image showing ER localization of GFP. Asterisks indicate the position of nuclei. The wild-type cb5 C-terminal sequence is shown. (B) Red BODIPY-C12 staining of a representative larval stage L4 animal. Imaging conditions are identical to that used in Fig. 2. (C and D) The single-copy transgene hjSi87[vha-6p::gfp::dgat-2::cb5mut] partially supported LD expansion in daf-22(ok693); dgat-2(hj44) mutant animals. (C) A representative image showing partial LD localization of GFP. Asterisks indicate the position of nuclei. The cb5 C-terminal sequence substituted with four charged residues (red) is shown. (D) Red BODIPY-C12 staining of a representative larval stage L4 animal. Expanded LDs are marked by white arrowheads. Imaging conditions are identical to that used in Fig. 2. Bars, 10 µm. (E) Quantification of total volumes of BODIPY-positive structures that were >3 µm in diameter in the second intestinal segment of larval stage L4 animals. Data for daf-22 and daf-22; dgat-2 were reproduced from Fig. 2 G and shown here for comparison. For each strain, a total of 20 animals were imaged at two independent times, except for daf-22; Si[dgat-2::cb5mut]; dgat-2 (n = 29). Data were plotted as means ± SEM. (F) Relative DAG acyltransferase (DGAT) activity of wild-type and variant murine DGAT2 in yeast cell extracts. All variant DGAT2 proteins were expressed at comparable levels as shown in the Western blot. Data were obtained from duplicate assays of two independent experiments and normalized to bar 2. Means ± SEM. Asterisk shows no significant difference in one-way analysis of variance with Neuman-Keuls after testing. IB, immunoblot; WT, wild type.