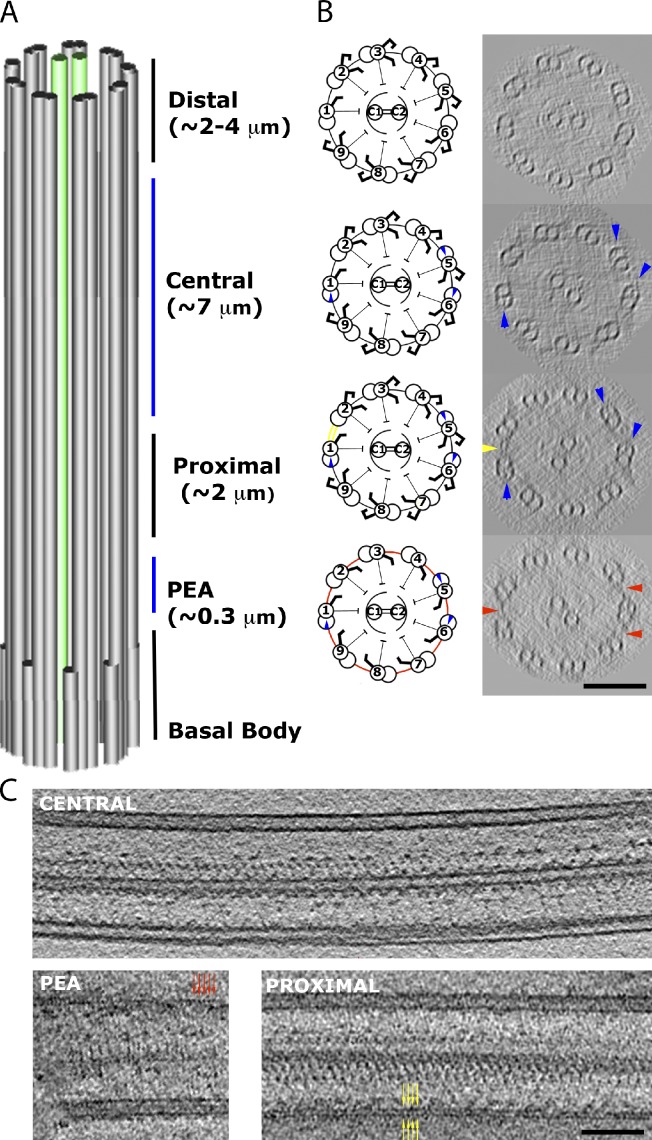
Figure 1.
Division of the complete Chlamydomonas axoneme. (A) The partitions of the axoneme into four regions: PEA, proximal, central, and distal. (B) Cartoons and representative 96-nm-thick cross-sections of each region from our tomograms, observed from base to tip of the axoneme. The markers of different regions are circumferential interdoublet linkers (red) in the PEA region, the 1–2 bridge (yellow) in the proximal region, and the beaks in MTD1, 5, and 6 (blue) in the central region. No beak was found in the distal region. As a result of the missing wedge effect in the raw tomogram, only three circumferential linkers roughly parallel to the optical axis are seen. Examination of all our data indicates that the circumferential linkers exist between every pair of MTDs in the PEA region, and they are absent from other regions. (C) Single tomographic slices showing the longitudinal sections of flagella in the central region (top), the PEA region (bottom left), and the proximal region (bottom right). The red and yellow arrows indicate a short span of the linkers in the PEA region and the 1–2 bridge, respectively. Bars, 100 nm.