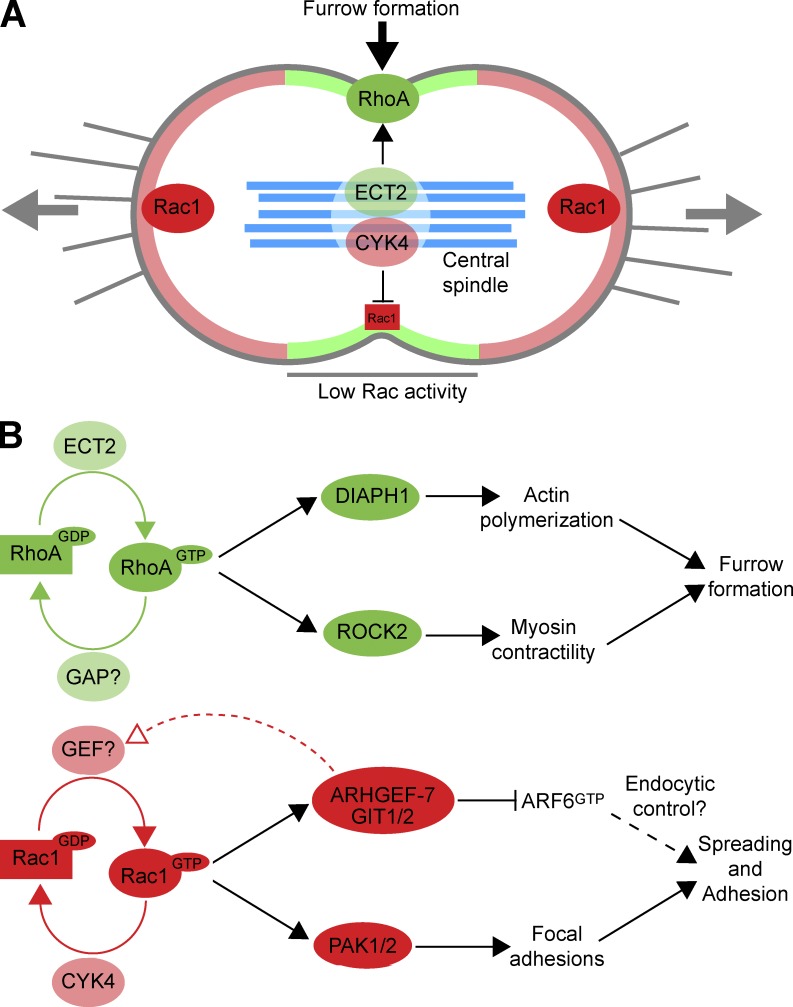
Figure 10.
A model for CYK4 regulation of Rac1 activity in anaphase. (A) At the onset of anaphase, cells adhere at the cell poles and contract in the equatorial region, driven by Rac1 and RhoA, respectively. The RhoA exchange factor ECT2 is enriched at the cell equator because of interactions with the MKlp1–CYK4 centralspindlin complex. This leads to local activation of RhoA in the furrow region (shaded pale green). Rac1 is inactivated in this region by the CYK4 GAP component of centralspindlin, creating a zone of low Rac1 activity. This does not occur at the cell poles, so Rac1 activity is higher in these regions (shaded pale red). Central spindle microtubules are shown in pale blue. (B) Regulatory and effector pathways for RhoA and Rac1 are summarized, together with the events they are known to control. The identity of the mitotic RhoA GAP remains to be assigned. GIT1/2 have been previously assigned as ARF6 GAPs and are therefore shown as inhibitors of ARF6 function. ARF6 has a complex function in cytokinesis together with Rab35 and modulates endocytic recycling (Chesneau et al., 2012).